Talk:Capacitive Measuring Methods: Difference between revisions
SLeithaeuser (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m (Protected "Talk:Capacitive Measuring Methods" ([edit=sysop] (indefinite) [move=sysop] (indefinite))) |
(No difference)
| |
Latest revision as of 08:35, 2 December 2012
Author: Hans-Jürgen Schwarz
back to Air Humidity Measurement
Abstract[edit]
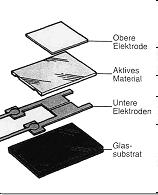
The measuring principle of the capacitive humidity sensor is based on changes in the capacitance of a thin polymer film, to absorb or release of water molecules.
The Sensor consists of:
- a glass substrate (mount),
- the lower electrodes,
- the active polymer film (e.g. cellulose acetate or polyamide),
- the water-vapor-permeable upper electrodes.
The quantity of moisture that is contained in the ambient air, penetrates the upper electrode of the humidity sensor in the form of water vapor and then reaches the active polymer film. The quantity of water vapor, which is absorbed by the polymer film, changes the electrical(???) properties of the sensor to such a degree, that the capacitance changes.
The change in capacitance is proportional to the change in relative humidity. It is evaluated by a downstream electronic controller(???) and converted into a standardized output signal.
Due to the special design and the low mass of the capacitive humidity sensor, fast response times are achieved. Furthermore, the sensors are relatively insensitive to light soiling and dust. In order to protect the surface from mechanical damage, the sensors are usually enclosed in a plastic housing. For the application in extreme humidity conditions, condensation safe appliances are available.
Capacitive measuring methods are not used when high concentrations of corrosive gases or solvents are present.
The standard measuring range for capacitive humidity sensors, is predominantly at 10-90% relative humidity (RH). The measuring range of high quality devices may be between 0% and 100% RH.
A major advantage of the capacitive measuring method, is the wide temperature range in which humidity measurements can be performed. For instance, some modern, industrially used humidity sensors allow for measuring humidity and temperature with a standardized output signal at -40°C to 180°C.
The capacitive measuring method has another advantage: due to the purely electrical measurement, the humidity sensors can be equipped with the latest high quality microprocessor technology that offer a wide range of features. Gas pressures and air velocities have little influence on the capacitive humidity sensor, therefore versions are available that work in pressure-loaded systems between 0-100 bar.
The accuracy varies between devices and ranges between ± 2% and ± 5% RH. Sometimes an accuracy of even ± 1% RH may be achieved.
Advantages:
- Inexpensive, quick and precise
- Wide measuring range (0 .. 100 %RH, -4 .. +180 ºC
- Long-term stability
- Small, portable devices
- Does not depend on air pressure
- Measuring is possible without maintenance, even at temperatures below freezing
Disadvantages:
- Limited long-term stability
- Susceptible to condensation and corrosive media
SLeithaeuser 17:51, 27 October 2012 (CEST)