Non-contact temperature measurement: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
{{underConstruction}} | |||
<!-- | |||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
| Line 53: | Line 56: | ||
<biblist/> | <biblist/> | ||
--> | |||
[[Category:IR Thermography]][[Category:Temperature Measurement]][[Category:Schwarz,Hans-Jürgen]][[Category:R-HSchwarz]][[Category:R-SLaue]][[Category:inProgress]] | [[Category:IR Thermography]][[Category:Temperature Measurement]][[Category:Schwarz,Hans-Jürgen]][[Category:R-HSchwarz]][[Category:R-SLaue]][[Category:inProgress]] | ||
Revision as of 16:19, 27 November 2012
Author: Hans-Jürgen Schwarz
English version by Sandra Leithäuser
back to Temperature Measurement
| This article will be released soon. |
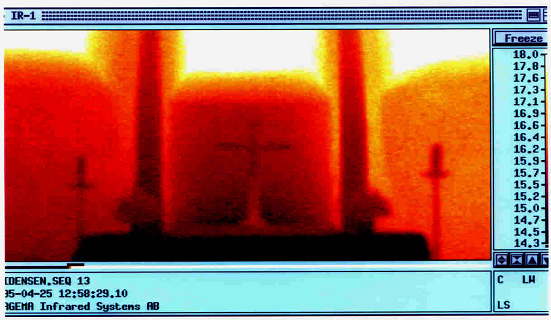
The infrared camera is based on the same principles as the infrared thermometer. However, the camera makes a scan of a specific image area, using a cooled semiconductor detector. The individual measurement pixels are electronically converted into a picture. The infrared shows things that are otherwise not visible to the naked eye. Infrared cameras produce images of the invisible infrared or heat radiation and make precise non-contact temperature measurement possible.
| Thermography uses a camera to visualize the thermal energy radiated from an object. . |
Temperature can be displayed in different shades of gray or different colors. The infrared camera gives an overview of all parts of the building and, e.g. thermal bridges can easily be recognized.
WebLinks
Literatur
| [Bernhard:2003] | Bernhard, Frank (eds.) (2003): Technische Temperaturmessung. Physikalische und meßtechnische Grundlagen, Sensoren und Meßverfahren, Meßfehler und Kalibrierung, Springer, Berlin |  |
-->