Polarized light microscopy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
The | The identification of salts with a polarized light microscope is briefly described and includes the advantages and disadvantages of the method. | ||
== Introduction == | |||
== | [[Image:MgSO4 Kristallisationsvideo.ogg|thumb|right|Magnesium sulfate crystallization under crossed polars and red I]]<br> Polarized light microscopy <bib id="Wuelfert:1999" /><bib id="McCrone.etal:1984" /> is used especially for the examination of anisotropic (birefringent) objects <ref>http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artnov08/rd-crystals.html, gesehen 19.11.2009</ref>. This microscope differs from ordinary microscopes by having a precisely centered rotating stage and the polarizing and analyzing filters introduced (below and above the stage, respectively) in the light path so that the object can be observed under plane polarized light or under crossed polarizers. One filter, referred to as the polarizer, is located in the light path beneath the sample slide. Through it the object is illuminated with linear polarized light. The second filter, called the analyzer, is situated in the observation beam path allowing the analysis of the linear polarized light modified by the object. When the polarizer and the analyzer are "crossed" (referred to as crossed polars) it means that there is a 90° difference in the vibration plane of the light allowed through them. When no sample is present, or an isotropic material is in the beam path, no light will come through. | ||
In polarized light microscopy the direct (orthoscopic) or indirect (conoscopic) approach can be applied. | |||
The orthoscopic approach is equivalent to ordinary microscopy. When the analyzer is switched on anisotropic bodies appear. Depending on their orientation, thickness and the value of the [[Birefringence|birefringence]]<ref>http://e3.pphysik.uni-dortmund.de/~suter/Vorlesung/Physik_B3_SS03/6.5_Polarisation.pdf, gesehen 19.11.2009</ref><ref>http://www.gemmologie.at/mediaCache/Doppelbrechung_270385.pdf, gesehen 19.11.2009</ref><ref>http://www.physik.uni-jena.de/inst/iao/applets/doppelbrechung/doppelbrechung.html, gesehen 19.11.2009</ref> anisotropic bodies appear in the interference color that corresponds to the path difference between the ordinary and extraordinary ray. The [[Light Refraction Index Determination|light refraction]] of salt minerals can be estimated relatively easily, when the [[refraction of light|refraction index]] of the immersion medium or oil is known. | |||
[[Image: | [[Image:Raithetalort-kon-eng.jpg|thumb|600px|center|'''A''':In the orthoscopic light path (luke optical path) of older polarization microscopes the lens produces a vertically and laterally inverted intermediate picture of the thin section. This is further increased with the eyepiece (A-2). In modern polarization microscopes<ref> http://www.igw.uni-jena.de/mineral/downloads/polarisationsmikr.pdf gesehen 16.07.2010</ref> the object is located in the lower focal plane of the lens, causing it to be reproduced to infinity. The real intermediate image, visible through the eyepiece (A-1) is produced by an additional lens in the tube (tube lens). By this display method a parallel beam path is created between the tube lens and the eyepiece, creating ideal conditions for an interference-free introduction of analyzers, compensators, or reflectors, and also allowing for a better aberration correction. | ||
'''B''': In the conoscopic beam path (pupillary light pathway) | '''B''': In the conoscopic beam path (pupillary light pathway), the reproduction of parallel light beams of the light cone takes place in the upper focal plane of the lens. The developing interference image (in the case of anisotropic crystals) can be magnified with an Amici- Bertrand lens. | ||
If no Amici-Bertrand lens is present, the interference image can also be seen through a diopter that can be inserted into the tube instead of the eyepiece.<bib id="Raith.etal: | If no Amici-Bertrand lens is present, the interference image can also be seen through a diopter that can be inserted into the tube instead of the eyepiece.<bib id="Raith.etal:2012"/> ]] | ||
[[Polarization microscope:Conoscopy|Conoscopic approach]]: By switching on an additional lens (Amici-Bertrand lens) or by removal of an eyepiece, the back focal plane of the objective is pictured in the intermediate image plane, seen through the eyepiece. | |||
While in the orthoscopic approach every image point corresponds to an object point, in the conoscopic approach every image point corresponds to a parallel beam of light. Therefore the image gives information about the directionality of the birefringence (as far as it can be detected by the aperture). Consequently, this method allows to determine whether a crystal is optically uniaxial or biaxial and whether it is optically positive or negative. | |||
For a detailed description of microscopic mineral analysis see <bib id="Raith.etal: | For a detailed description of microscopic mineral analysis see <bib id="McCrone.etal:1984" /> or <bib id="Raith.etal:2012" /><ref>http://www.dmg-home.de/pdf/Guide-print%20quality.pdf</ref>. | ||
<br> '''Advantage:''' | <br> '''Advantage:''' | ||
Polarized light microscopy is a quick and convenient method for the [[ | Polarized light microscopy is a quick and convenient method for the [[Microscopic identification of salts| identification of salts]]. The mineralogy and chemistry of salts is determined. Basic polarizing microscopes are portable and can be used in any location, hence ''sensitive'' salts can be identified on site. | ||
<br> '''Disadvantage:''' | <br> '''Disadvantage:''' | ||
| Line 36: | Line 38: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
== | == Literature == | ||
<biblist /> | <biblist /> | ||
[[Category:Light Microscopy]] [[Category:Husen,Anika]] [[Category:Schwarz,Hans-Jürgen]] [[Category:R-MSteiger]] [[Category:R-CBlaeuer]] [[Category: | [[Category:Light Microscopy]] [[Category:Husen,Anika]] [[Category:Schwarz,Hans-Jürgen]] [[Category:R-MSteiger]] [[Category:R-CBlaeuer]] [[Category: approved]] | ||
Revision as of 10:42, 20 September 2013
Authors: Hans-Jürgen Schwarz, Anika Husen
back to Analysis of Salts
Abstract[edit]
The identification of salts with a polarized light microscope is briefly described and includes the advantages and disadvantages of the method.
Introduction[edit]
Polarized light microscopy [Wuelfert:1999]Title: Der Blick ins Bild
Author: Wülfert, Stefan [McCrone.etal:1984]Title: Polarized light microscopy
[McCrone.etal:1984]Title: Polarized light microscopy
Author: McCrone, W. C.,; McCrone, L. B. ; Delly, J. G. is used especially for the examination of anisotropic (birefringent) objects [1]. This microscope differs from ordinary microscopes by having a precisely centered rotating stage and the polarizing and analyzing filters introduced (below and above the stage, respectively) in the light path so that the object can be observed under plane polarized light or under crossed polarizers. One filter, referred to as the polarizer, is located in the light path beneath the sample slide. Through it the object is illuminated with linear polarized light. The second filter, called the analyzer, is situated in the observation beam path allowing the analysis of the linear polarized light modified by the object. When the polarizer and the analyzer are "crossed" (referred to as crossed polars) it means that there is a 90° difference in the vibration plane of the light allowed through them. When no sample is present, or an isotropic material is in the beam path, no light will come through.
is used especially for the examination of anisotropic (birefringent) objects [1]. This microscope differs from ordinary microscopes by having a precisely centered rotating stage and the polarizing and analyzing filters introduced (below and above the stage, respectively) in the light path so that the object can be observed under plane polarized light or under crossed polarizers. One filter, referred to as the polarizer, is located in the light path beneath the sample slide. Through it the object is illuminated with linear polarized light. The second filter, called the analyzer, is situated in the observation beam path allowing the analysis of the linear polarized light modified by the object. When the polarizer and the analyzer are "crossed" (referred to as crossed polars) it means that there is a 90° difference in the vibration plane of the light allowed through them. When no sample is present, or an isotropic material is in the beam path, no light will come through.
In polarized light microscopy the direct (orthoscopic) or indirect (conoscopic) approach can be applied. The orthoscopic approach is equivalent to ordinary microscopy. When the analyzer is switched on anisotropic bodies appear. Depending on their orientation, thickness and the value of the birefringence[2][3][4] anisotropic bodies appear in the interference color that corresponds to the path difference between the ordinary and extraordinary ray. The light refraction of salt minerals can be estimated relatively easily, when the refraction index of the immersion medium or oil is known.
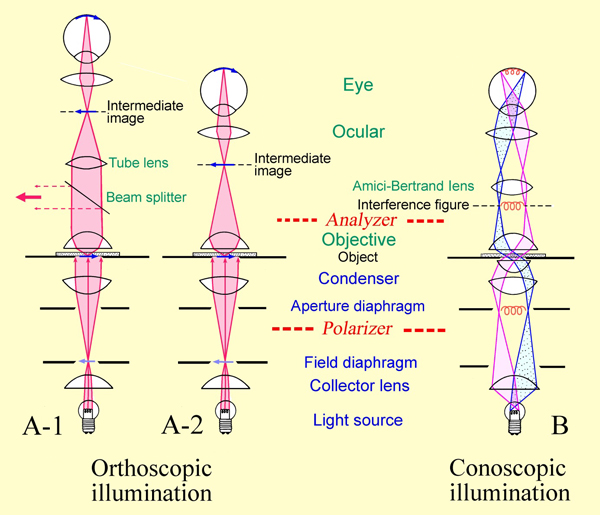
Author: Raith, Michael M.; Raase, Peter; Reinhardt, Jürgen

Conoscopic approach: By switching on an additional lens (Amici-Bertrand lens) or by removal of an eyepiece, the back focal plane of the objective is pictured in the intermediate image plane, seen through the eyepiece. While in the orthoscopic approach every image point corresponds to an object point, in the conoscopic approach every image point corresponds to a parallel beam of light. Therefore the image gives information about the directionality of the birefringence (as far as it can be detected by the aperture). Consequently, this method allows to determine whether a crystal is optically uniaxial or biaxial and whether it is optically positive or negative.
For a detailed description of microscopic mineral analysis see [McCrone.etal:1984]Title: Polarized light microscopy
Author: McCrone, W. C.,; McCrone, L. B. ; Delly, J. G. or [Raith.etal:2012]Title: Guide to Thin Section Microscopy, Second Edition
or [Raith.etal:2012]Title: Guide to Thin Section Microscopy, Second Edition
Author: Raith, Michael M.; Raase, Peter; Reinhardt, Jürgen [6].
[6].
Advantage:
Polarized light microscopy is a quick and convenient method for the identification of salts. The mineralogy and chemistry of salts is determined. Basic polarizing microscopes are portable and can be used in any location, hence sensitive salts can be identified on site.
Disadvantage:
Some salts are difficult to identify. Quantitative identification is not possible.
Weblinks[edit]
- ↑ http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artnov08/rd-crystals.html, gesehen 19.11.2009
- ↑ http://e3.pphysik.uni-dortmund.de/~suter/Vorlesung/Physik_B3_SS03/6.5_Polarisation.pdf, gesehen 19.11.2009
- ↑ http://www.gemmologie.at/mediaCache/Doppelbrechung_270385.pdf, gesehen 19.11.2009
- ↑ http://www.physik.uni-jena.de/inst/iao/applets/doppelbrechung/doppelbrechung.html, gesehen 19.11.2009
- ↑ http://www.igw.uni-jena.de/mineral/downloads/polarisationsmikr.pdf gesehen 16.07.2010
- ↑ http://www.dmg-home.de/pdf/Guide-print%20quality.pdf
Literature[edit]
| [McCrone.etal:1984] | McCrone, W. C.,; McCrone, L. B. ; Delly, J. G. (1984): Polarized light microscopy, McCrone Research Institute, Chicago, 9th ed. 1995 |  |
| [Raith.etal:2012] | Raith, Michael M.; Raase, Peter; Reinhardt, Jürgen (2012): Guide to Thin Section Microscopy, Second Edition, online publication, Url, |  |
| [Wuelfert:1999] | Wülfert, Stefan (1999): Der Blick ins Bild, Ravensburger Buchverlag |  |