Calicum nitrate: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
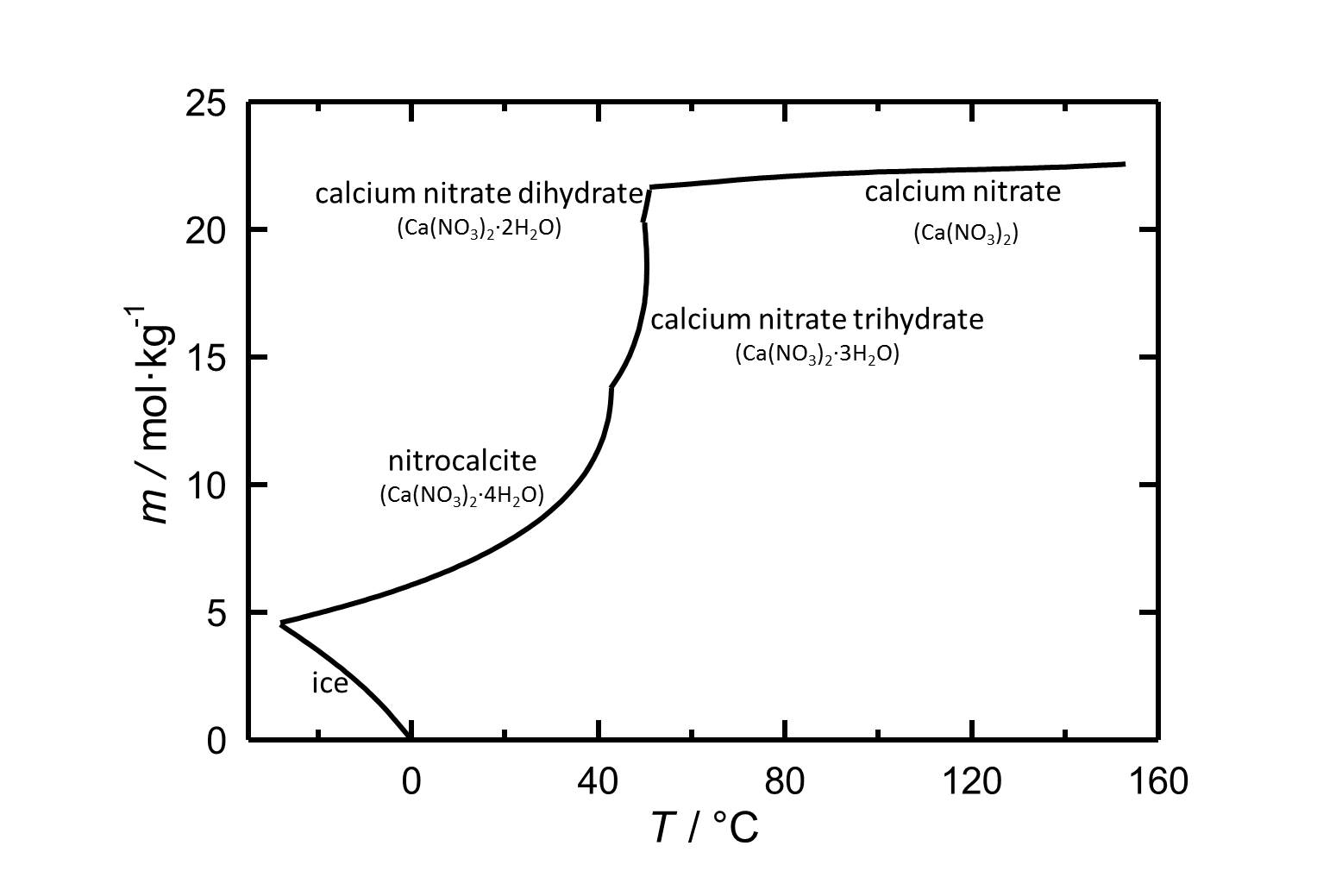
[[Image:Solubility of calcium nitrate in water.jpg|thumb|left|800px|Figure 1: Solubility of calcium nitrate in water. The molality ''m'' [n(Ca(NO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>•xH<sub>2</sub>O)•kg(H<sub>2</sub>O)<sup>-1</sup>] is plotted against the temperature.]] | [[Image:Solubility of calcium nitrate in water.jpg|thumb|left|800px|Figure 1: Solubility of calcium nitrate in water. The molality ''m'' [n(Ca(NO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>•xH<sub>2</sub>O)•kg(H<sub>2</sub>O)<sup>-1</sup>] is plotted against the temperature.]] | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
Under standard conditions the tetrahydrate of calcium nitrate [[Nitrocalcite]] is the stable phase. With its relatively high solubility in water it is a highly soluble salt. The temperature dependence of the solubility is shown in the solubility diagram, where in parts the solubility increases extremely with increasing temperature. The dehydrations to the Trihydrate, Dihydrate and at least to the anhydrous calcium nitrate take place at 43 °C, 49.5 °C and 51 °C, respectively. | |||
==Hygroscopcity== | ==Hygroscopcity== | ||
Revision as of 14:18, 25 February 2015
Author: Amelie Stahlbuhk
back to Nitrate
| This article will be released soon. |
| Calicum nitrate | |
| Mineralogical name | Calcium nitrate |
| Chemical name | Calcium nitrate |
| Trivial name | |
| Chemical formula | Ca(NO3)2 |
| Other forms | Ca(NO3)2•2H2O (Calcium nitrate dihydrate) Ca(NO3)2•3H2O (Calcium nitrate trihydrate) Ca(NO3)2•4H2O (Nitrocalcite) |
| Crystal system | |
| Crystal structure | |
| Deliquescence humidity 20°C | |
| Solubility (g/l) at 20°C | |
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.483 g/cm3 |
| Molar volume | 66.09 cm3/mol |
| Molar weight | 164.09 g/mol |
| Transparency | |
| Cleavage | |
| Crystal habit | |
| Twinning | |
| Phase transition | |
| Chemical behavior | |
| Comments | |
| Crystal Optics | |
| Refractive Indices | |
| Birefringence | |
| Optical Orientation | |
| Pleochroism | |
| Dispersion | |
| Used Literature | |
| [Robie.etal:1978]Title: Thermodynamic properties of minerals and related substances at 298.15 K and 1 bar pressure and higher temperatures Author: Robie R.A., Hemingway B.S.; Fisher J.A. 
| |
Abstract[edit]
In this article the salt calcium nitrate will be presented. The behavior regarding solubility an hygroscopicity will be shown for caclium nitrate and the different hydrate states.
Solubility[edit]
Under standard conditions the tetrahydrate of calcium nitrate Nitrocalcite is the stable phase. With its relatively high solubility in water it is a highly soluble salt. The temperature dependence of the solubility is shown in the solubility diagram, where in parts the solubility increases extremely with increasing temperature. The dehydrations to the Trihydrate, Dihydrate and at least to the anhydrous calcium nitrate take place at 43 °C, 49.5 °C and 51 °C, respectively.
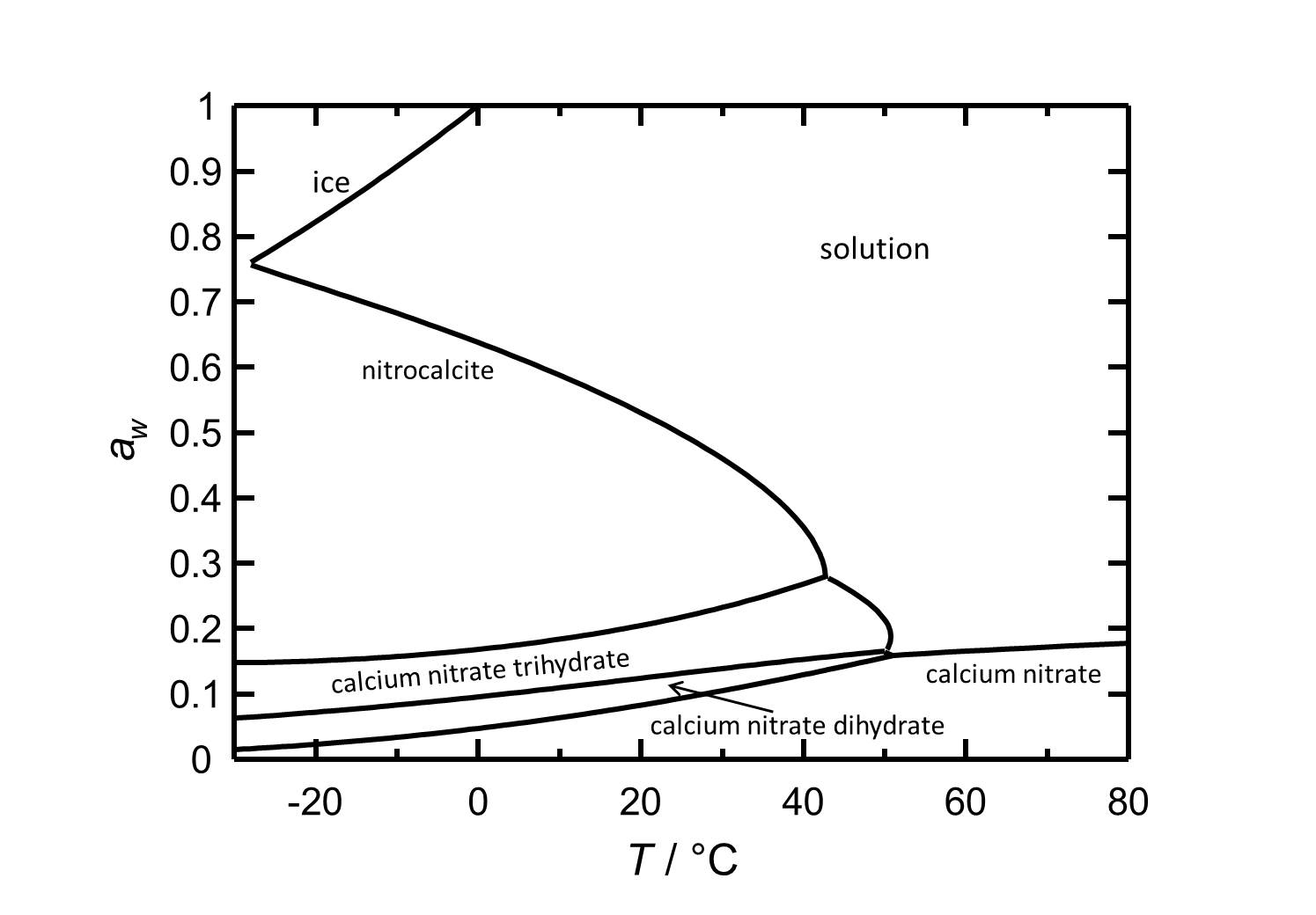
Hygroscopcity[edit]
References[edit]
Literature[edit]
| [Robie.etal:1978] | Robie R.A., Hemingway B.S.; Fisher J.A. (1978): Thermodynamic properties of minerals and related substances at 298.15 K and 1 bar pressure and higher temperatures. In: U.S. Geol. Surv. Bull, 1452 () |  |