Calcite: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (50 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Authors: [[user:Hschwarz|Hans-Jürgen Schwarz ]], Nils Mainusch, [[user:ECharola|A. Elena Charola ]] | |||
<br> | |||
English Translation by [[user:SLeithaeuser|Sandra Leithäuser]]<br> | |||
<br>back to [[Carbonate|Carbonate]] | |||
{{Infobox_Salt | {{Infobox_Salt | ||
|Footnote =<ref>http://webmineral.com/data/Calcite.shtml viewed on 09/06/2011</ref><ref>http://www.mindat.org/min-859.html viewed on 09/06/2011</ref> | |Footnote =<ref>http://webmineral.com/data/Calcite.shtml viewed on 09/06/2011</ref><ref>http://www.mindat.org/min-859.html viewed on 09/06/2011</ref> | ||
|photo = | |photo =[[Image:Calcit Kristalle Musterplatte.jpg|300px]] | ||
|mineralogical_Name = Calcite | |mineralogical_Name = Calcite | ||
|chemical_Name =Calcium carbonate | |chemical_Name =Calcium carbonate | ||
|Trivial_Name = | |Trivial_Name =Iceland spar, calcite spar | ||
|chemical_Formula =CaCO<sub>3</sub> | |chemical_Formula =CaCO<sub>3</sub> | ||
|Hydratforms =CaCO<sub>3</sub>•H<sub>2</sub>O<br>CaCO<sub>3</sub>•6H<sub>2</sub>O | |Hydratforms =CaCO<sub>3</sub>•H<sub>2</sub>O<br>CaCO<sub>3</sub>•6H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
| Line 10: | Line 15: | ||
|Crystal_Structure = | |Crystal_Structure = | ||
|Deliqueszenzhumidity = | |Deliqueszenzhumidity = | ||
|Solubility = | |Solubility = 0.014 g/l (25°C) | ||
|Density =2 | |Density =2.72 g/cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
|MolVolume =100 | |MolVolume = | ||
|Molweight =100.09 g/mol | |||
|Transparency =transparent to opaque | |Transparency =transparent to opaque | ||
|Cleavage =perfect | |Cleavage =perfect | ||
|Crystal_Habit = | |Crystal_Habit = | ||
|Twinning = | |Twinning = | ||
|Refractive_Indices =n<sub>o</sub> = 1 | |Refractive_Indices =n<sub>o</sub> = 1.658<br>n<sub>e</sub> = 1.486 | ||
|Birefringence =Δ = 0 | |Birefringence =Δ = 0.172 | ||
|optical_Orientation =negative | |optical_Orientation =negative | ||
|Pleochroism = | |Pleochroism = | ||
| Line 25: | Line 30: | ||
|Phase_Transition = | |Phase_Transition = | ||
|chemBehavior = | |chemBehavior = | ||
|Comments = | |Comments =well soluble in 2M HCl | ||
|Literaure = | |||
}} | }} | ||
<!-- | |||
== Abstract == | |||
== Introduction == | |||
<br> | |||
< | |||
[[Category:Calcite]][[Category:Carbonate]][[Category:Salt]][[Category: | == Preface == | ||
--> | |||
== Occurrence of calcite<br> == | |||
Calcium carbonate occurs as a natural mineral in three polymorphs, calcite, aragonite, and vaterite, the last two being metastable. Vaterite, the least stable one transforms into calcite at low temperatures and into aragonite at higher temperatures (approx. 60ºC). Vaterite can be detected in bone and gallstones, while aragonite is formed in biological processes, for example, egg- or mollusk-shells. Iceland spar, calcite spar or calc-spar is a very pure, transparent variety of calcium carbonate which shows a strong birefringence, was discovered and scientifically explained by C. Huygens in the 17th century.<br><br> | |||
== Information on calcite relevant to its formation during weathering == | |||
=== Solubility === | |||
The system CaCO<sub>3</sub>– H<sub>2</sub>O:<br>The two known hydrated forms of calcium carbonate, mono and hexa-hydrate, only exist under special circumstances and dehydrate under normal ambient air-conditions to calcite.<br> | |||
Calcite is barely soluble in water. The influence of temperature on solubility is low. | |||
{|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="30%" align="center" class="wikitable" | |||
|+''Table 1: Calcite: Solubility in dependance of temperature [Data from H. J. Schwarz 1996 and Stark/Stürmer 1993] <bib id="Stark.etal:1996" />'' | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor = "#F0F0F0" align="center"| '''18°C''' | |||
|bgcolor = "#F0F0F0" align="center"| '''25°C''' | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor = "#FFFFEO" align="center"| 0,015g/l | |||
|bgcolor = "#FFFFEO" align="center"| 0,014 g/l | |||
|} | |||
However, if water contains CO<sub>2</sub>, the solubility of calcite increases considerably because of the formation of carbonic acid that will react forming soluble calcium bicarbonate, Ca(HCO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>. This is a slow reaction but over centuries of water flowing through limestone, some of it is slowly carried away and deposited when the water evaporates, as for example in the limestone caves where stalactites and stalactites form. When a drop of saturated solution of calcite is exposed to air, the water evaporates and a film or calcite is formed around the drop. As more of the saturated solutions filters out, it will cover the film of calcite allow the formation of a thicker film, while a new water surface is exposed and a new film created resulting in concentric tubes as shown in the SEM figures below. Larger crystals will develop towards the evaporating surface linking the concentric films to each other. Eventually, the whole stalactite may fill with a crystalline growth of calcite. | |||
A similar phenomenon can be observed in the formation of small stalactites, the most common ones being those that form on concrete bridges. In this case, the mechanism is different: water percolating through concrete will dissolve the unreacted calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)<sub>2</sub>, in it. This is a fast reaction compared to the slow dissolution of calcite. When the alkaline solution reaches the exterior, it will react with the CO<sub>2</sub> from the air, another very fast reaction. This explains why the stalactite from concrete grow so fast, and why, except in special cases, they are small. | |||
===Deterioration Potential=== | |||
The low solubility of CaCO<sub>3</sub> precludes it from being a "deteriorating" salt. However, because of its slow dissolution as mentioned above, in some cases it may result in the formation of hard calcite concretions, for example, in marble fountains with water sprays that enhance water evaporation so that concretions form over the edge of the basin or any sculptures washed over by the water. Similar disfigurement can be seen in concrete structures either in stains or the formation of stalatites at the edge of cracks or fissures where more water can percolate. Even along the edges of joints filled with Portland cement, particularly if these got wet before they set completely. | |||
<!--<br> | |||
The system CaCO<sub>3</sub>– H<sub>2</sub>O:<br>The two known hydrate stages of calcium carbonate, mono and hexa-hydrate, only exist under special circumstances and dehydrate under normal ambient air-conditions.<br> | |||
<!-- === Crystallization pressure === | |||
=== Conversion reaction === | |||
== Analytical identification == --> | |||
== Microscopy<br> == | |||
'''Laboratory examination:'''<br> Calcite is only slightly soluble in water, therefore recrystallization cannot be initiated. | |||
<br> '''Refractive indices:''' n<sub>0</sub> = 1.658, n<sub>E</sub> = 1.486 <br>'''Birefringence''': Δ = max. 0,172<br>'''Crystal class''': trigonal<br> | |||
<br> '''Polarized light microscopic examination:'''<br> | |||
Calcite crystals growing during the setting of lime mortars, renders or in lime-paints are very poorly formed and seldom can be identified by their morphology using light microscopy. In these samples, calcite appears as a matrix of fine, rounded particles, in which developed tabular rhombohedra, the characteristic shape for calcite, rarely appear. | |||
If calcite sample materials stem from another source than calcite-spar, e.g., chalk or mussels, then significantly larger equidimensional particles can appear. Strongly elongated particles, laths, needles or crystal aggregates are rarely found. | |||
The very high birefringence leads to interference phenomena, even with very small particles. In addition the strong relief changes are very noticeable, especially when using an immersion medium with a refractive index near n<sub>O</sub> – value of 1,658. Since calcite is optically uni-axial, independent of the orientation and the viewing direction, in one of the two normal positions it always displays a fixed refractive index value, being effective at n<sub>D</sub> = 1,658. | |||
<br>'''Positive identification:'''<br> | |||
Calcite can clearly be identified, if the following characteristics are observed:<br> | |||
*Low solubility in water | |||
*Sensitivity to acids | |||
*Very strong birefringence | |||
*High relief in most immersion media<br> | |||
*When using an embedding medium with a refractive index of 1,662 it reveals a strong relief change, wherein a crystal nearly disappears in the normal position, when n<sub>o</sub>-refractive index is effective <br> | |||
*Only parallel and symmetrical extinction is observable | |||
<br clear="all"> | |||
{|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="80%" align="left" class="wikitable" | |||
|+''Table 2: Salt phases, with chemical and optical properties similar to calcite'' | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor = "#F0F0F0"| '''Salt phase''' | |||
|bgcolor = "#F0F0F0"| '''Distinguishing features to calcite''' | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor = "#F7F7F7"| '''Dolomite''' MgCa(CO<sub>3</sub>)2 | |||
|bgcolor = "#FFFFEO"| Both indices above 1.5 | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor = "#F7F7F7"| '''Magnesite''' MgCO<sub>3</sub> | |||
|bgcolor = "#FFFFEO"| Both indices above 1.5, n<sub>o</sub>- Index with 1.7-1.719 significantly higher than calcite. | |||
|} | |||
<br clear="all"> | |||
<!-- | |||
== X-ray diffraction == | |||
== Raman-Stectroscopy == | |||
== DTA / TG == | |||
== IR-Spectroscopy == | |||
= How to deal with calcite damage = | |||
--> | |||
== Calcite in Pictures == | |||
<!-- === On the object === | |||
=== Under the polarizing microscope === --> | |||
=== Under the scanning electron microscope (SEM) === | |||
<gallery caption=" " widths="200px" heights="150px" perrow="3"> | |||
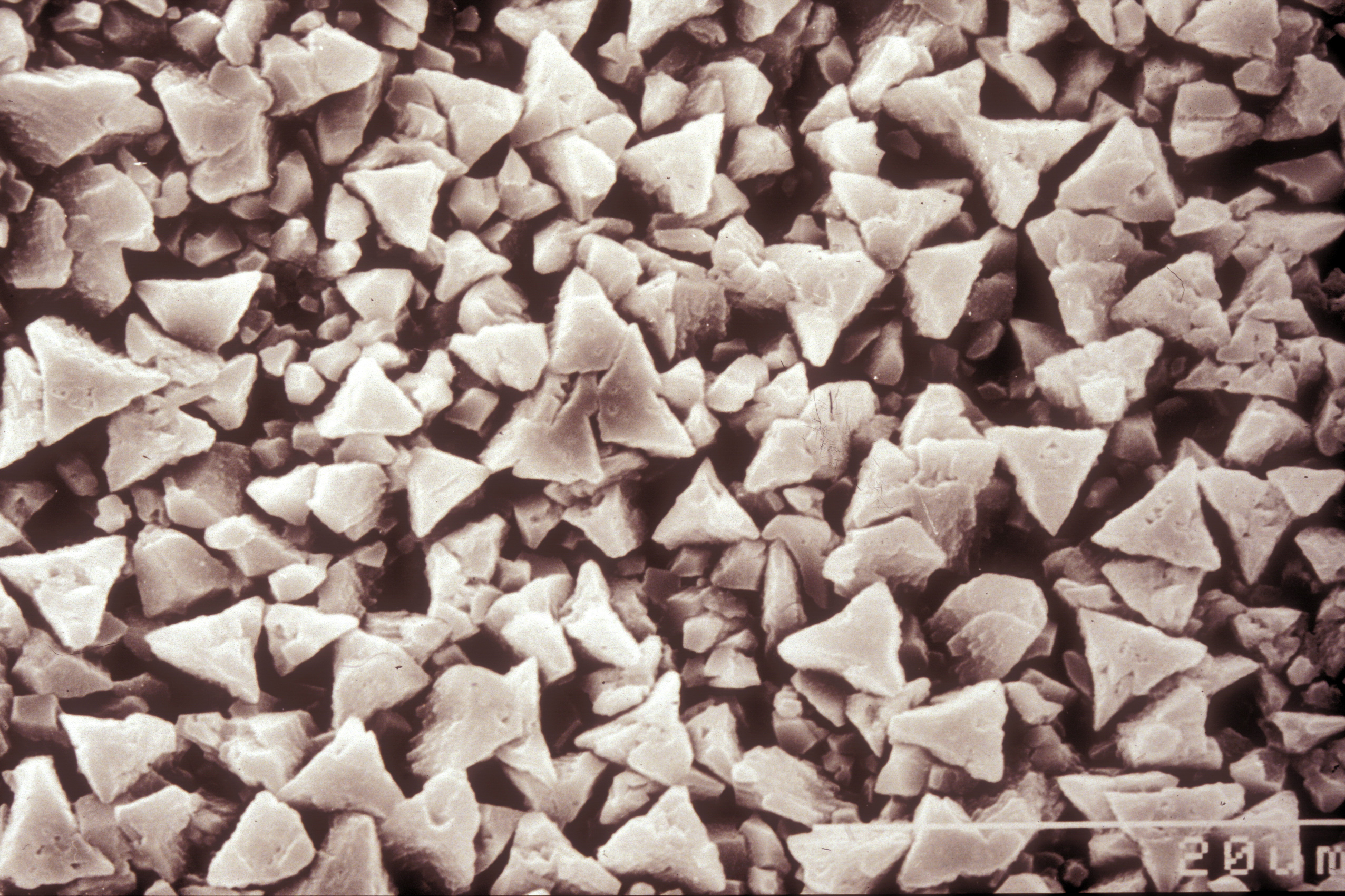
Image:Calcit Kristalle Musterplatte.jpg| Calcite crystals on a sample plate | |||
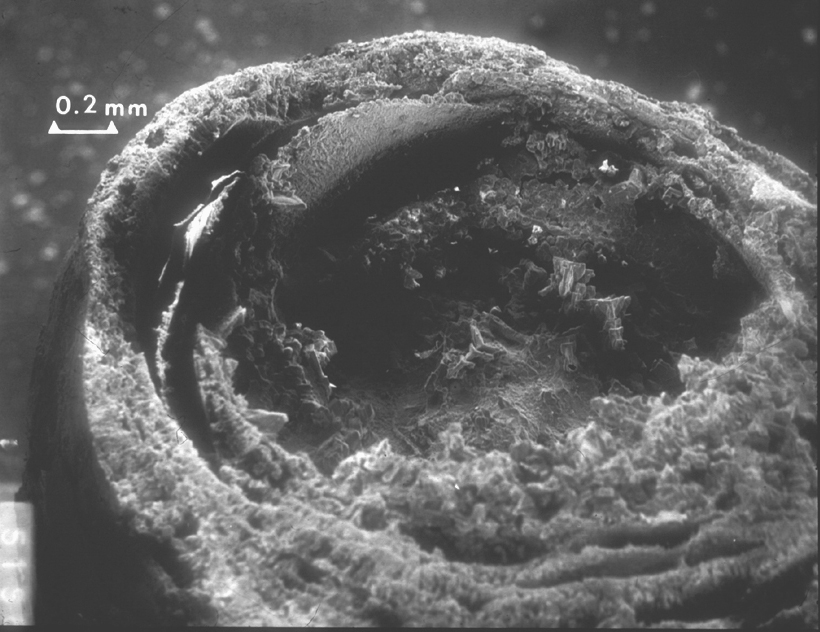
Image:Lincoln-Mem-stalactite-20xLsmall OK.jpg |SEM photo showing a cross section of a calcium carbonate stalactite formed by water percolation through concrete. Note that the stalactite is formed by concentric "tubes". | |||
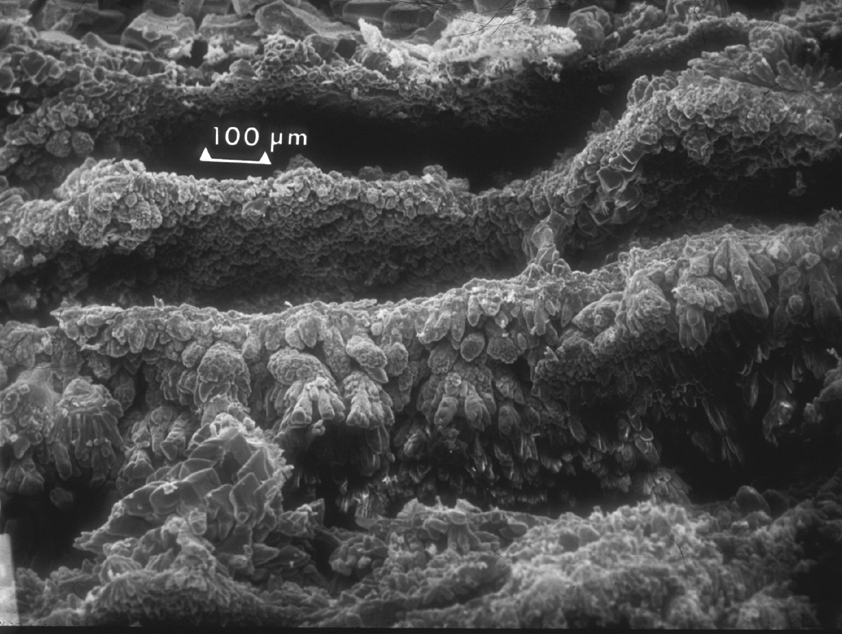
Image:Lincoln Mem stal-100x-Lsmall OK.jpg |Detail of the concentric growth of the "tubes" that conform the stalactive. | |||
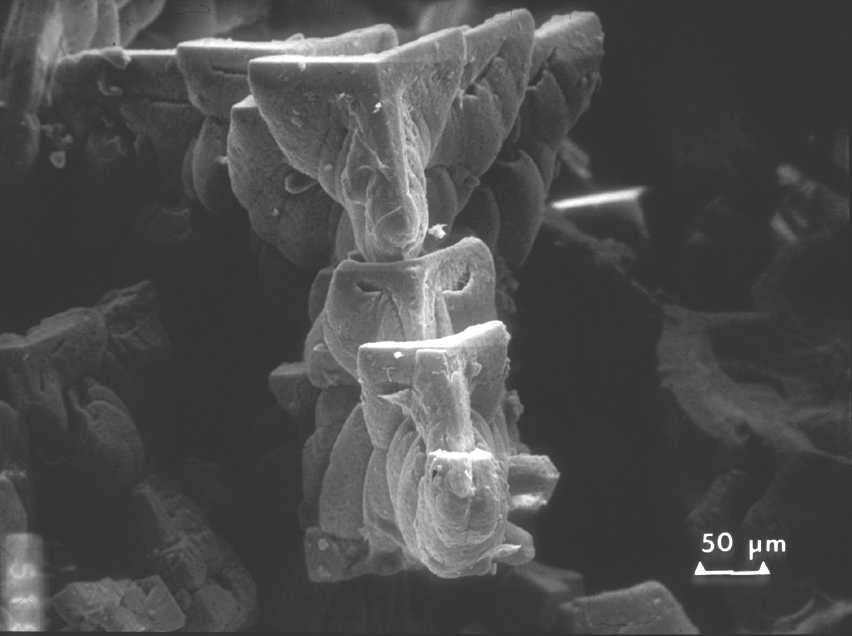
Image:Lincoln-Mem stal-200x-Lsmall OK.jpg |Detail of the crystals that developed in the center of the stalactive showing the trigonal shape of the calcite crystals. | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Weblinks<br> == | |||
<references/><br> | |||
== Literature == | |||
<biblist /> | |||
'''More Literature in the bibliography:''' | |||
<bibprint filter=" title:%calcite%"/> | |||
[[Category:Calcite]] [[Category:Schwarz,Hans-Jürgen]] [[Category:R-MSteiger]] [[Category: approved]] [[Category:Carbonate]] [[Category:Salt ]][[Category:List]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:22, 15 February 2015
Authors: Hans-Jürgen Schwarz , Nils Mainusch, A. Elena Charola
English Translation by Sandra Leithäuser
back to Carbonate
| Calcite[1][2] | |

| |
| Mineralogical name | Calcite |
| Chemical name | Calcium carbonate |
| Trivial name | Iceland spar, calcite spar |
| Chemical formula | CaCO3 |
| Other forms | CaCO3•H2O CaCO3•6H2O |
| Crystal system | trigonal |
| Crystal structure | |
| Deliquescence humidity 20°C | |
| Solubility (g/l) at 20°C | 0.014 g/l (25°C) |
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.72 g/cm3 |
| Molar volume | |
| Molar weight | 100.09 g/mol |
| Transparency | transparent to opaque |
| Cleavage | perfect |
| Crystal habit | |
| Twinning | |
| Phase transition | |
| Chemical behavior | |
| Comments | well soluble in 2M HCl |
| Crystal Optics | |
| Refractive Indices | no = 1.658 ne = 1.486 |
| Birefringence | Δ = 0.172 |
| Optical Orientation | negative |
| Pleochroism | |
| Dispersion | |
| Used Literature | |
| {{{Literature}}} | |
Occurrence of calcite
[edit]
Calcium carbonate occurs as a natural mineral in three polymorphs, calcite, aragonite, and vaterite, the last two being metastable. Vaterite, the least stable one transforms into calcite at low temperatures and into aragonite at higher temperatures (approx. 60ºC). Vaterite can be detected in bone and gallstones, while aragonite is formed in biological processes, for example, egg- or mollusk-shells. Iceland spar, calcite spar or calc-spar is a very pure, transparent variety of calcium carbonate which shows a strong birefringence, was discovered and scientifically explained by C. Huygens in the 17th century.
Information on calcite relevant to its formation during weathering[edit]
Solubility[edit]
The system CaCO3– H2O:
The two known hydrated forms of calcium carbonate, mono and hexa-hydrate, only exist under special circumstances and dehydrate under normal ambient air-conditions to calcite.
Calcite is barely soluble in water. The influence of temperature on solubility is low.
| 18°C | 25°C |
| 0,015g/l | 0,014 g/l |
However, if water contains CO2, the solubility of calcite increases considerably because of the formation of carbonic acid that will react forming soluble calcium bicarbonate, Ca(HCO3)2. This is a slow reaction but over centuries of water flowing through limestone, some of it is slowly carried away and deposited when the water evaporates, as for example in the limestone caves where stalactites and stalactites form. When a drop of saturated solution of calcite is exposed to air, the water evaporates and a film or calcite is formed around the drop. As more of the saturated solutions filters out, it will cover the film of calcite allow the formation of a thicker film, while a new water surface is exposed and a new film created resulting in concentric tubes as shown in the SEM figures below. Larger crystals will develop towards the evaporating surface linking the concentric films to each other. Eventually, the whole stalactite may fill with a crystalline growth of calcite.
A similar phenomenon can be observed in the formation of small stalactites, the most common ones being those that form on concrete bridges. In this case, the mechanism is different: water percolating through concrete will dissolve the unreacted calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2, in it. This is a fast reaction compared to the slow dissolution of calcite. When the alkaline solution reaches the exterior, it will react with the CO2 from the air, another very fast reaction. This explains why the stalactite from concrete grow so fast, and why, except in special cases, they are small.
Deterioration Potential[edit]
The low solubility of CaCO3 precludes it from being a "deteriorating" salt. However, because of its slow dissolution as mentioned above, in some cases it may result in the formation of hard calcite concretions, for example, in marble fountains with water sprays that enhance water evaporation so that concretions form over the edge of the basin or any sculptures washed over by the water. Similar disfigurement can be seen in concrete structures either in stains or the formation of stalatites at the edge of cracks or fissures where more water can percolate. Even along the edges of joints filled with Portland cement, particularly if these got wet before they set completely.
Microscopy
[edit]
Laboratory examination:
Calcite is only slightly soluble in water, therefore recrystallization cannot be initiated.
Refractive indices: n0 = 1.658, nE = 1.486
Birefringence: Δ = max. 0,172
Crystal class: trigonal
Polarized light microscopic examination:
Calcite crystals growing during the setting of lime mortars, renders or in lime-paints are very poorly formed and seldom can be identified by their morphology using light microscopy. In these samples, calcite appears as a matrix of fine, rounded particles, in which developed tabular rhombohedra, the characteristic shape for calcite, rarely appear.
If calcite sample materials stem from another source than calcite-spar, e.g., chalk or mussels, then significantly larger equidimensional particles can appear. Strongly elongated particles, laths, needles or crystal aggregates are rarely found.
The very high birefringence leads to interference phenomena, even with very small particles. In addition the strong relief changes are very noticeable, especially when using an immersion medium with a refractive index near nO – value of 1,658. Since calcite is optically uni-axial, independent of the orientation and the viewing direction, in one of the two normal positions it always displays a fixed refractive index value, being effective at nD = 1,658.
Positive identification:
Calcite can clearly be identified, if the following characteristics are observed:
- Low solubility in water
- Sensitivity to acids
- Very strong birefringence
- High relief in most immersion media
- When using an embedding medium with a refractive index of 1,662 it reveals a strong relief change, wherein a crystal nearly disappears in the normal position, when no-refractive index is effective
- Only parallel and symmetrical extinction is observable
| Salt phase | Distinguishing features to calcite |
| Dolomite MgCa(CO3)2 | Both indices above 1.5 |
| Magnesite MgCO3 | Both indices above 1.5, no- Index with 1.7-1.719 significantly higher than calcite. |
Calcite in Pictures[edit]
Under the scanning electron microscope (SEM)[edit]
Weblinks
[edit]
- ↑ http://webmineral.com/data/Calcite.shtml viewed on 09/06/2011
- ↑ http://www.mindat.org/min-859.html viewed on 09/06/2011
Literature[edit]
| [Stark.etal:1996] | Stark, Jochen; Stürmer, Sylvia (1996): Bauschädliche Salze, Bauhaus-Univ. Weimar |  |
More Literature in the bibliography:
| [Astilleros.etal:2000] | Astilleros, J. M.; Pina, C. M.; Fernandez-Diaz, L.; Putnis, A. (2000): The effect of barium on calcite "{101-4}" surfaces during growth. In: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64 (17), 2965-2972, Url |  |
| [Foner.etal:1983] | (1983): Simple method for the determination of gypsum, with some observations on the solubilities of gypsum, anhydrite, calcite and dolomite. In: Analyst, 108 (), 615-620 |  |
| [Lea.etal:2001] | Lea, A. S.; Amonette, J. E.; Baer, D. R.; Liang, Y.; Colton, N. G. (2001): Microscopic effects of carbonate, manganese, and strontium ions on calcite dissolution. In: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65 (3), 369-379 |  |
| [Mastromei.etal:1999] | Mastromei, G.; Biagiotti, L.; Daly, S.; Perito, B.; Tiano, P. (1999): Stone reinforcement by bio-mediated calcite crystal precipitation. In: Ciferri, O.; Tiano, P.; Mastromei, G. (eds.): International Conference on Microbiology and Conservation, 253-256. |  |
| [Plummer:1982] | Plummer, L. N. (1982): The solubilities of calcite, aragonite and vaterite in CO2-H2O solutions between 0 and 90°C, and an evaluation of the aqueous model for the system CaCO3-CO2-H2O. In: Geochimica et Cosmochimica et Acta, 46 (6), 1011-1040 |  |
| [Rothrock:1925] | Rothrock, E. P. (1925): On the force of crystallization of calcite. In: Journal of Geology, 33 (1), 80-83, Url |  |
| [Ruiz-Agudo.etal:2009] | Ruiz-Agudo, E.; Putnis, C. V.; Jiménez-López, C.; Rodriguez-Navarro, C. (2009): An atomic force microscopy study of calcite dissolution in saline solutions: The role of magnesium ions. In: Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 73 (11), 3201--3217, 10.1016/j.gca.2009.03.016 |  |
| [Ruiz-Agudo.etal:2009a] | Rodriguez-Navarro, C.; Ruiz-Agudo, E.; Luque, A.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A. B. ; Ortega-Huertas, M. (2009): Thermal decomposition of calcite: Mechanisms of formation and textural evolution of CaO nanocrystals. In: American Mineralogist, 94 (4), 578--593, 10.2138/am.2009.3021 |  |
| [Ruiz-Agudo.etal:2010] | Ruiz-Agudo, E.; Kowacz, M.; Putnis, C. V.; Putnis, A. (2010): The role of background electrolytes on the kinetics and mechanism of calcite dissolution. In: Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 74 (4), 1256--1267, 10.1016/j.gca.2009.11.004 |  |
| [Ruiz-Agudo.etal:2011b] | Ruiz-Agudo, E.; Putnis, C. V.; Rodriguez-Navarro, C.; Putnis, A. (2011): Effect of pH on calcite growth at constant a Ca 2 + / a CO 3 2 - ratio and supersaturation. In: Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 75 (1), 284--296, 10.1016/j.gca.2010.09.034 |  |
| [Ruiz-Agudo.etal:2011c] | Ruiz-Agudo, Encarnación ; Putnis, Christine V.; Wang, Lijun ; Putnis, Andrew (2011): Specific effects of background electrolytes on the kinetics of step propagation during calcite growth. In: Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 75 (13), 3803--3814, 10.1016/j.gca.2011.04.012 |  |
| [Siegel.etal:1968] | Siegel, Frederic R.; Dort, Wakefield Jr.; Milton, Charles (1968): Thenardite, syngenite, gypsum, and calcite caliche from Southern Victoria Land, Antarctica. In: Geol. Soc. Amer., Spec. Paper. No., 101 (201) |  |
| [Skoulikidis.etal:1984a] | Skoulikidis, Theodore N.; Beloyannis, Nicholas (1984): Inversion of marble sulfation - reconversion of gypsum films into calcite on the surfaces of monuments and statues. In: Studies in Conservation, 29 (4), 197-204, Url |  |
| [Tiano.etal:1992] | Tiano, P.; Addadi, L.; Weiner, S. (1992): Stone reinforcement by induction of calcite crystals using organic matrix macromolecules. Feasibility study. In: Rodrigues, J. Delgado; Henriques, Fernando; Jeremias, F. Telmo (eds.): Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone, Lisbon Portugal, 15-18 June 1992 ,Laboratorio Nacional de Engenharia Civil 1317-1326. |  |
| [Tiano.etal:1999] | Tiano, P.; Biagiotti, L.; Mastromei, G. (1999): Bacterial bio-mediated calcite precipitation for monumental stones conservation: methods of evaluation. In: J. Microbiol. Methods, 36 (1), 139-145 |  |
| [Tiano:1995] | Tiano, P. (1995): Stone reinforcement by calcite crystal precipitation induced by organic matrix macromolecules. In: Studies in Conservation, 40 (3), 171-176 |  |
| [VergesBelmin:1994] | Verges-Belmin, V. (1994): Pseudomorphism of gypsum after calcite, a new textural feature accounting for the marble sulphation mechanism. In: Atmospheric Environment, 28 (2), 295-304 |  |
| [Wolf.etal:1992] | Wolf, Manfred; Rohde, Harald (1992): Solubility of calcite in mixed aqueous solutions of NaCl and KCl at 25 degrees C and CO2 partial pressures of about 1 kPa. In: Proceedings of the 7th international symposium on water rock interaction, 7 (), 195 |  |