Nitrocalcite: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Weblinks
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
== Solubility == | == Solubility == | ||
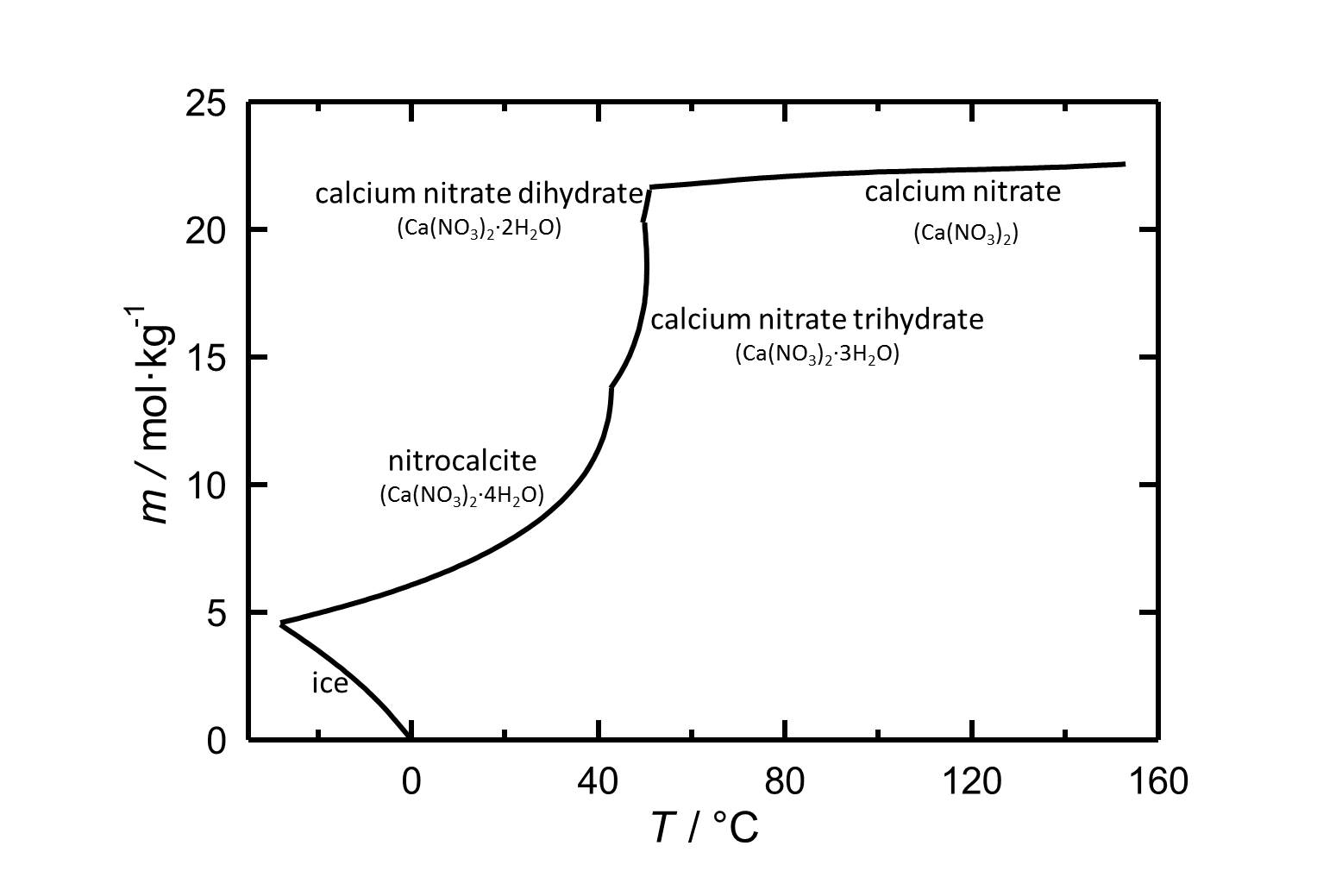
[[file:Solubility of calcium nitrate in water.jpg|thumb|800px|left|'''Figure 1''' Solubility of calcium nitrate in water. The molality ''m'' [n(Ca(NO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>•xH<sub>2</sub>O)•kg(H<sub>2</sub>O)<sup>-1</sup>] is plotted versus the temperature.]] | [[file:Solubility of calcium nitrate in water.jpg|thumb|800px|left|'''Figure 1''' Solubility of calcium nitrate in water. The molality ''m'' [n(Ca(NO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>•xH<sub>2</sub>O)•kg(H<sub>2</sub>O)<sup>-1</sup>] is plotted versus the temperature.]] | ||
</br> | |||
</br> | |||
</br> | |||
</br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br> | |||
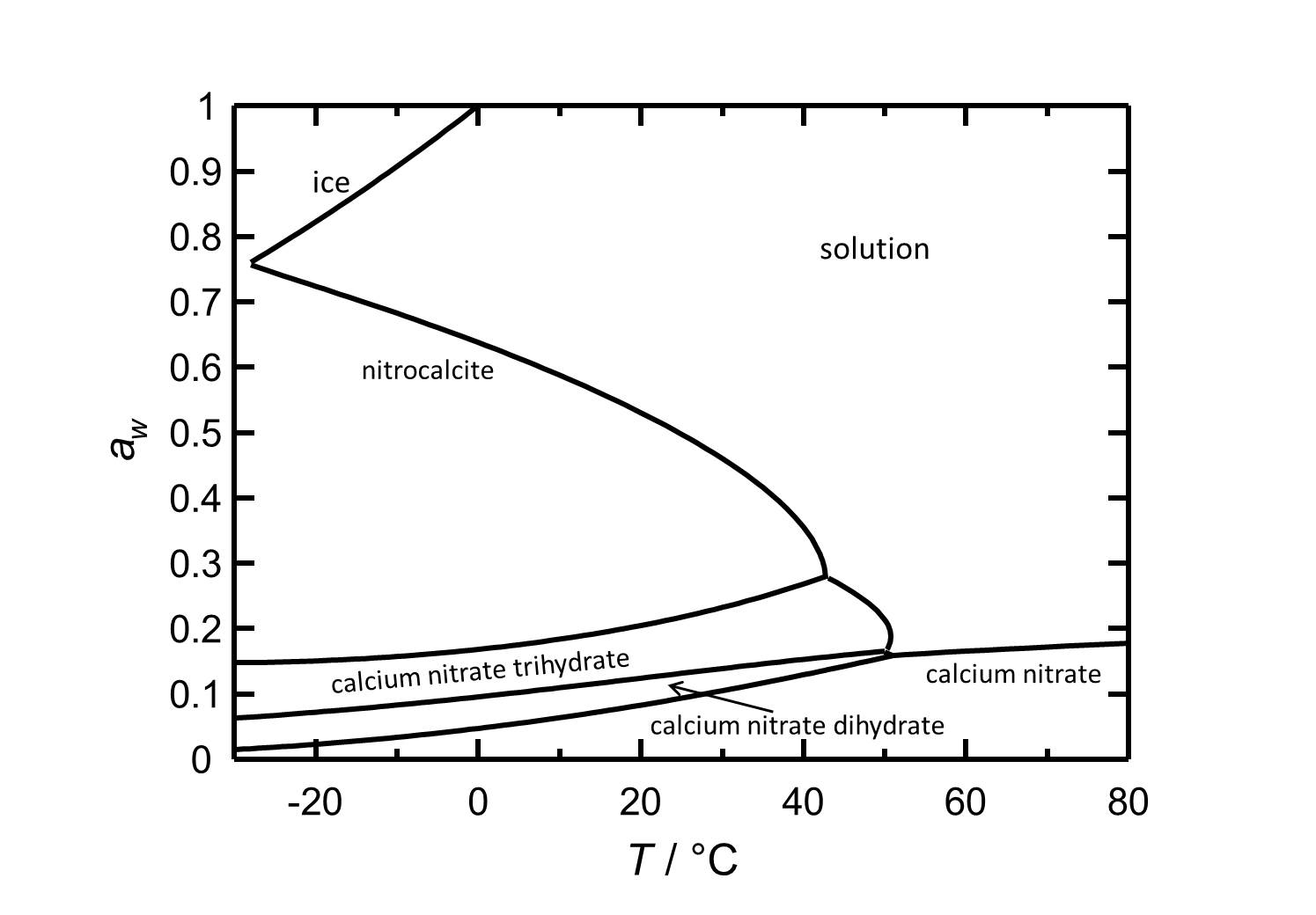
At 20 °C nitrocalcite is the stable phase of calcium nitrate. The salt has got a high solubilty in water and due to the temperature range of its stability it is relevant as a crystallizing phases under ambient conditions. | |||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
==Hygroscopicity== | ==Hygroscopicity== | ||
Latest revision as of 07:58, 3 May 2023
| Nitrocalcite[1] | |
| |
| Mineralogical name | Nitrocalcite |
| Chemical name | Calcium Nitrate Tetrahydrate |
| Trivial name | Nitrate of lime |
| Chemical formula | Ca(NO3)2•4H2O |
| Other forms | Ca(NO3)2•2H2O (calcium nitrate dihydrate) Ca(NO3)2•3H2O (calcium nitrate trihydrate) |
| Crystal system | monoclinic |
| Crystal structure | |
| Deliquescence humidity 20°C | 53.06% |
| Solubility (g/l) at 20°C | 7.726 mol/kg |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.82 g/cm3 |
| Molar volume | 129.8 cm3/mol |
| Molar weight | 236.15 g/mol |
| Transparency | transparent |
| Cleavage | |
| Crystal habit | |
| Twinning | |
| Phase transition | |
| Chemical behavior | |
| Comments | |
| Crystal Optics | |
| Refractive Indices | nx = 1.465 ny = 1.498 nz = 1.504 |
| Birefringence | Δ = 0.039 |
| Optical Orientation | negative |
| Pleochroism | |
| Dispersion | |
| Used Literature | |
| [Steiger.etal:2014]Title: Weathering and Deterioration Author: Steiger, Michael; Charola A. Elena; Sterflinger, Katja  [Broul.etal:1981]Title: Solubility in organic two component systems [Broul.etal:1981]Title: Solubility in organic two component systemsAuthor: Broul M., Nyvlt J.; Soehnel O. 
| |
back to Nitrate
Solubility[edit]
At 20 °C nitrocalcite is the stable phase of calcium nitrate. The salt has got a high solubilty in water and due to the temperature range of its stability it is relevant as a crystallizing phases under ambient conditions.
Hygroscopicity[edit]
| 0°C | 10°C | 20°C | 30°C | 40°C | 50°C |
| 63.8%r.h. | 58.8%r.h. | 53.1%r.h. | 46.0%r.h. | 35.5%r.h. | 21.3%r.h. (Ca(NO3)2•3H2O) |
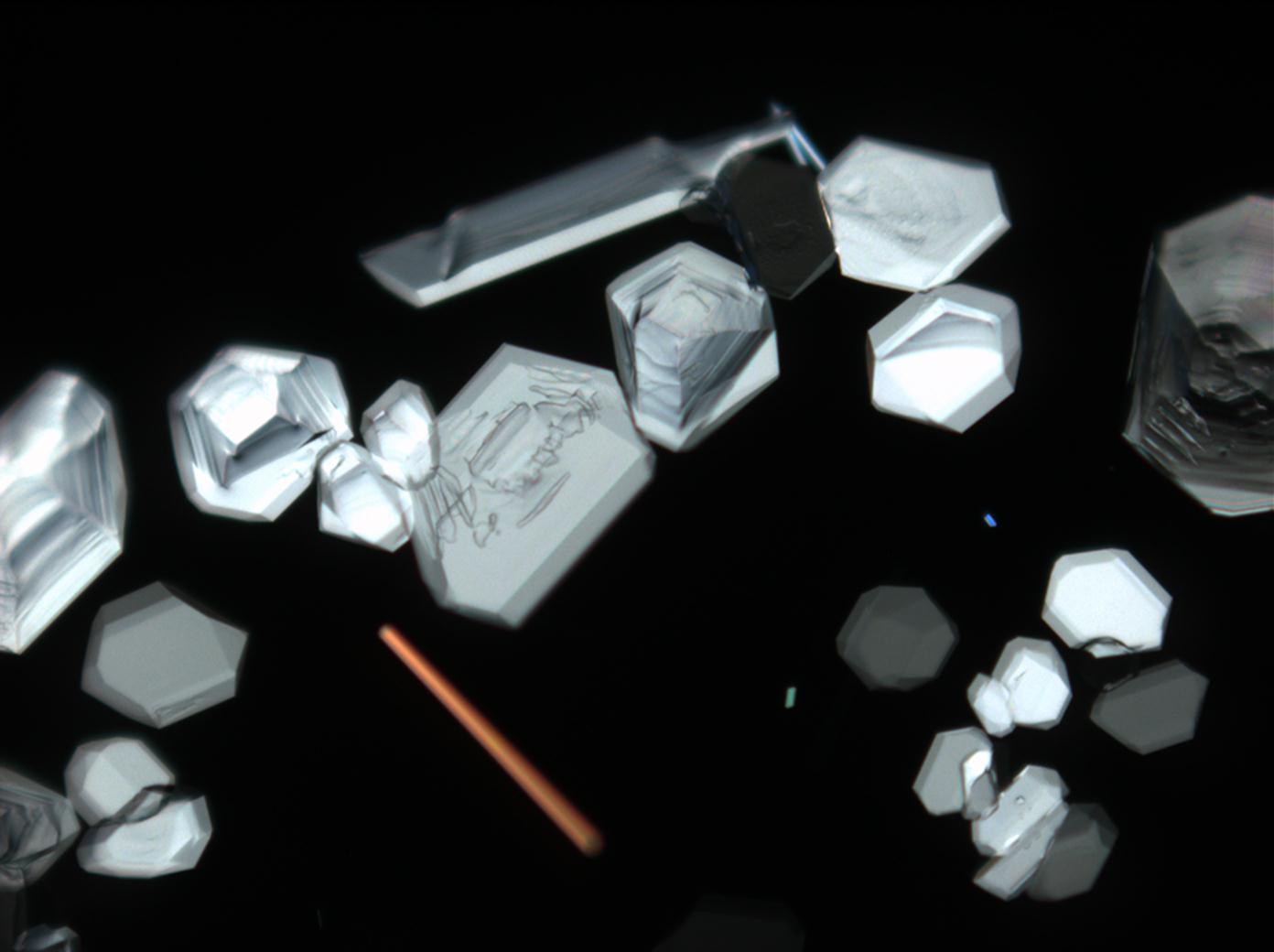
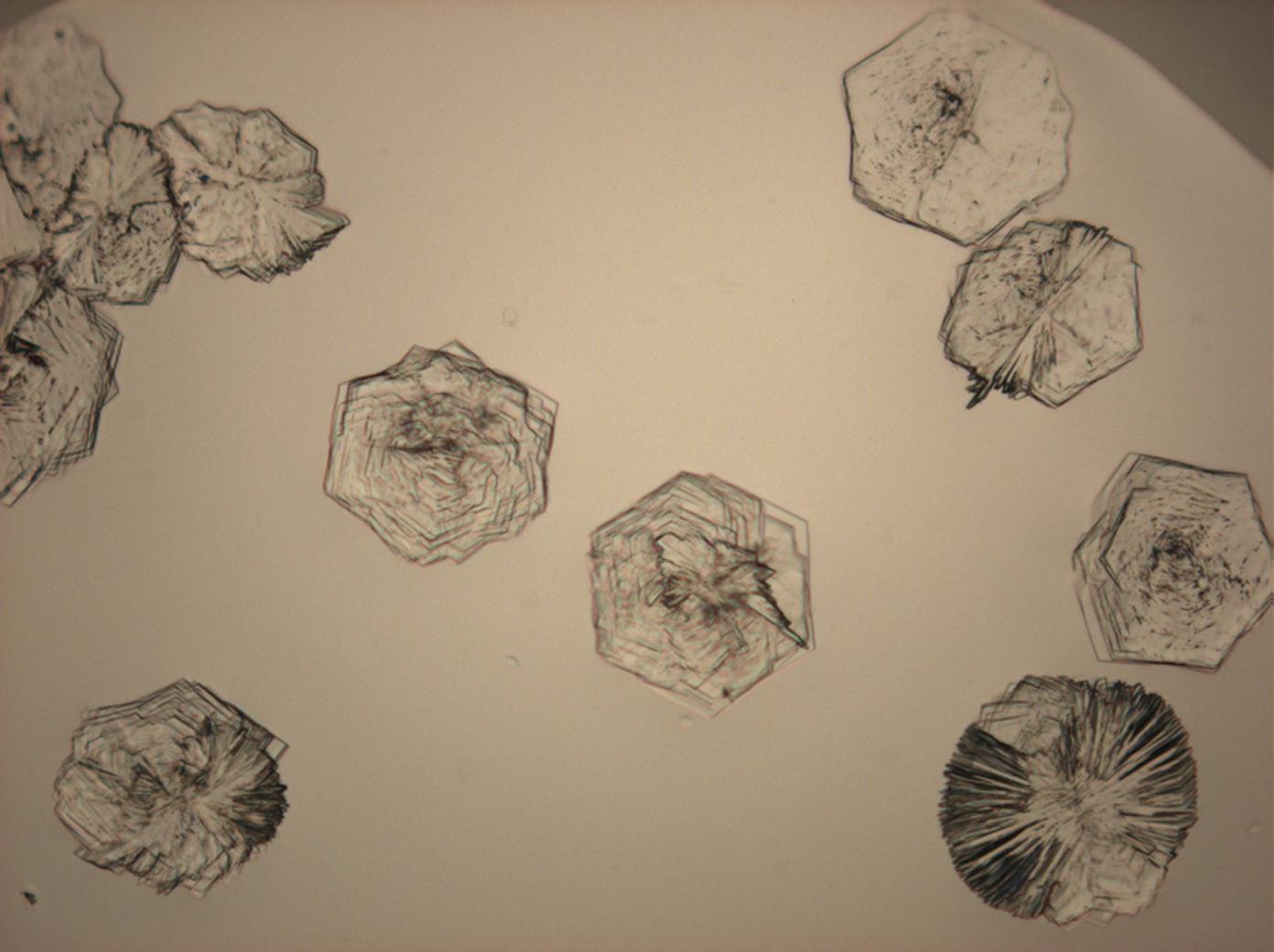
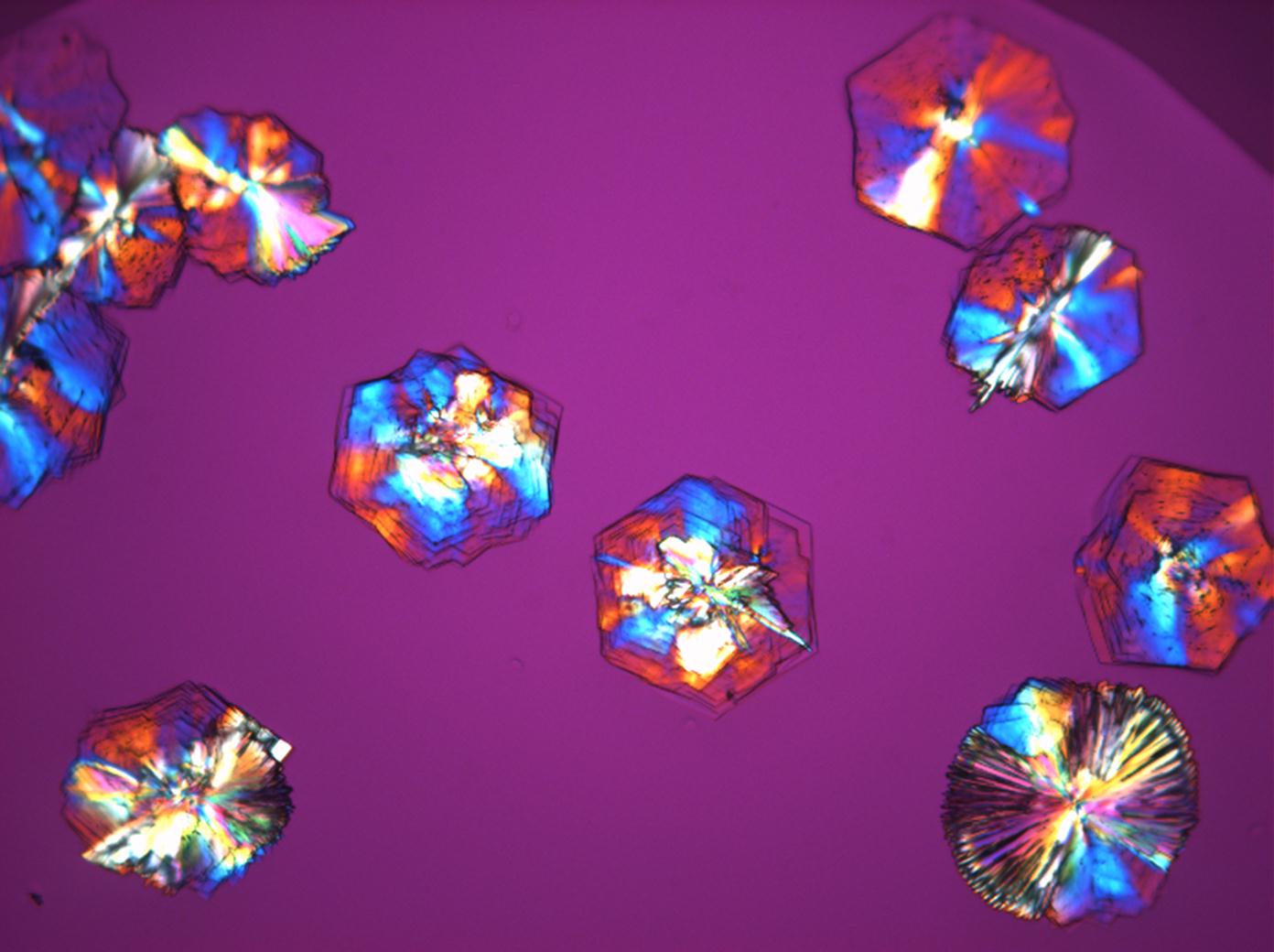
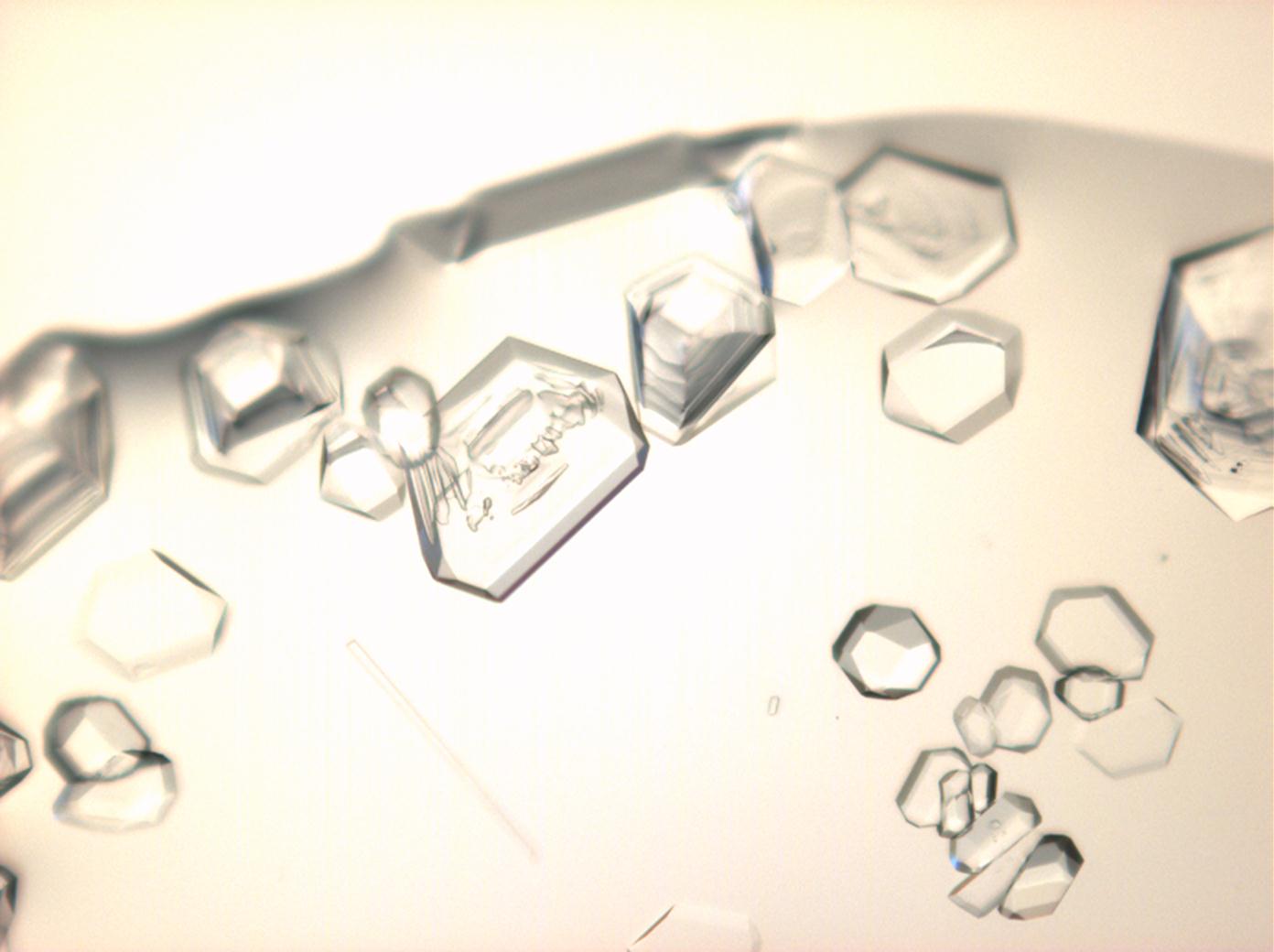
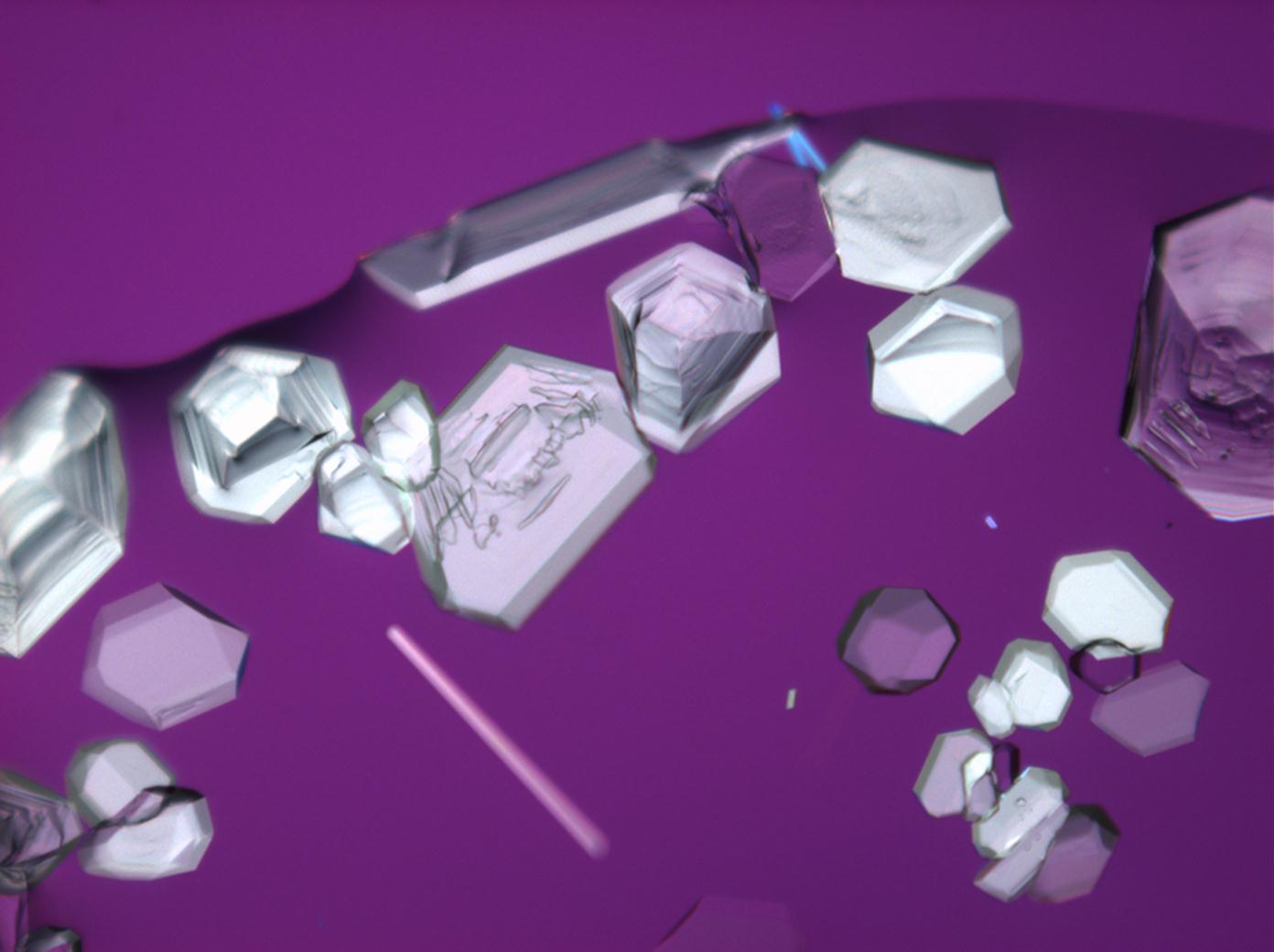
Under the polarizing microscope[edit]
- Crystallized from a saturated solution with ethanol addition
- Crystallized in a micro climate chamber
Weblinks
[edit]
- ↑ http://www.mindat.org/min-2919.html seen on 29.07.2010
Literature[edit]
| [Broul.etal:1981] | Elsevier (eds.) Broul M., Nyvlt J.; Soehnel O. (1981): Solubility in organic two component systems, Elsevier |  |
| [Steiger.etal:2014] | Steiger, Michael; Charola A. Elena; Sterflinger, Katja (2014): Weathering and Deterioration. In: Siegesmund S.; Snethlage R. (eds.): Stone in Architecture, Springer Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 223-316, 10.1007/978-3-642-45155-3_4. |  |