Deterioration Patterns Wallpaintings: Difference between revisions
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[file:Gipskruste Hygroskopisch.jpg|thumb|300px|left|Gypsum crust, hygroscopic, grave chamber Nehren]] | [[file:Gipskruste Hygroskopisch.jpg|thumb|300px|left|Gypsum crust, hygroscopic, grave chamber Nehren]] | ||
[[file:Salzkruste Hygroskopisch Nehren.jpg|thumb|300px|right|Gypsum crust, hygroscopic, grave chamber Nehren]] | [[file:Salzkruste Hygroskopisch Nehren.jpg|thumb|300px|right|Gypsum crust, hygroscopic, grave chamber Nehren]] | ||
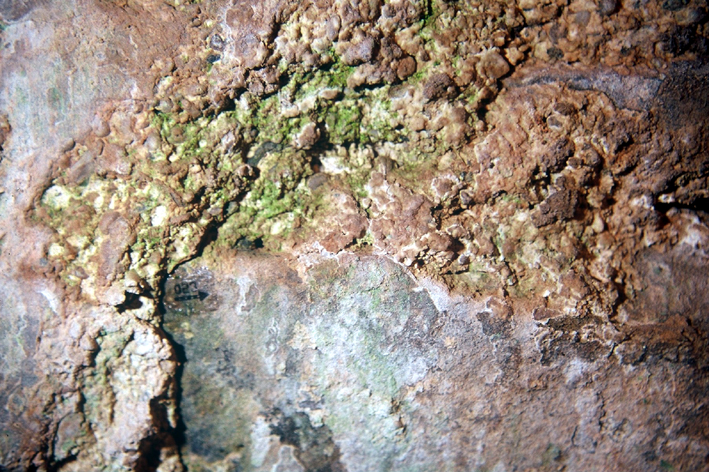
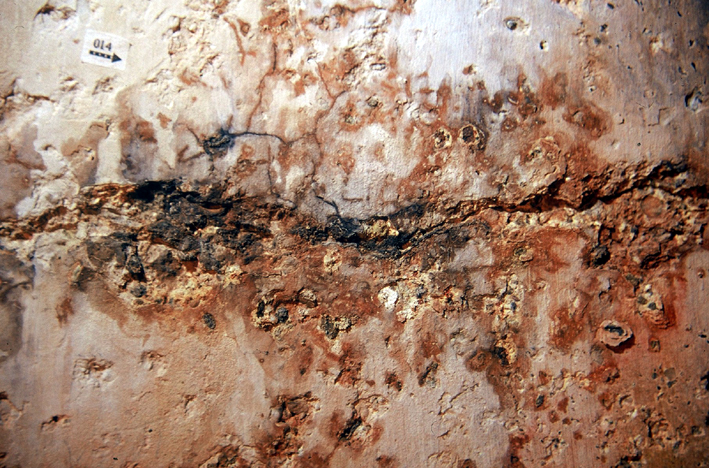
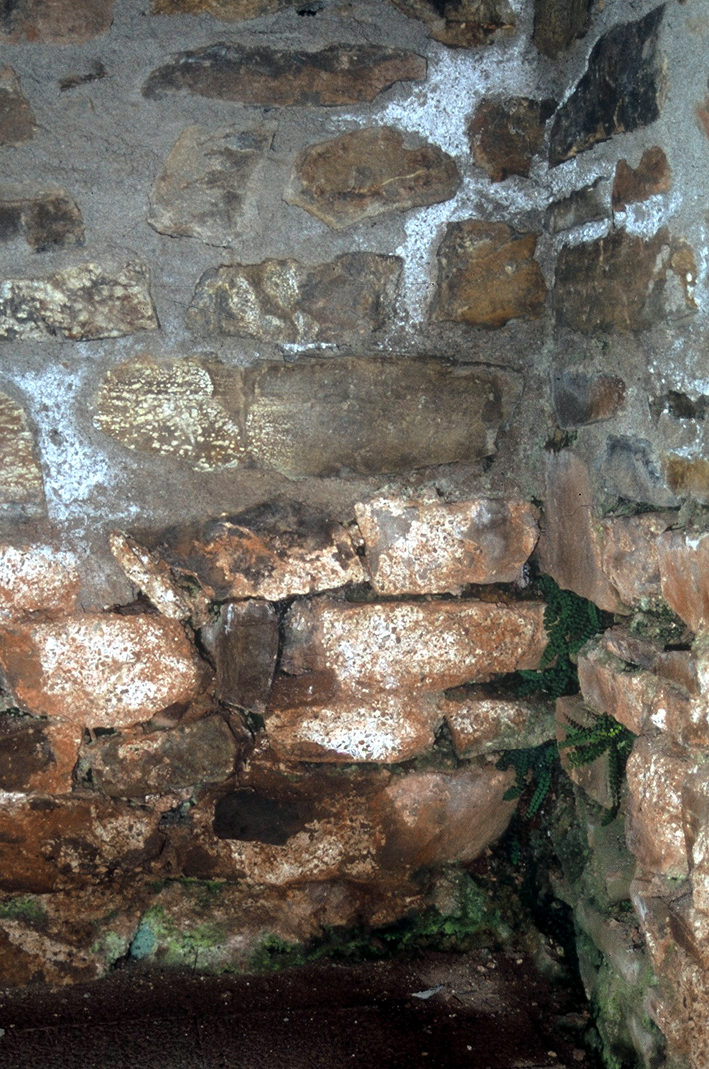
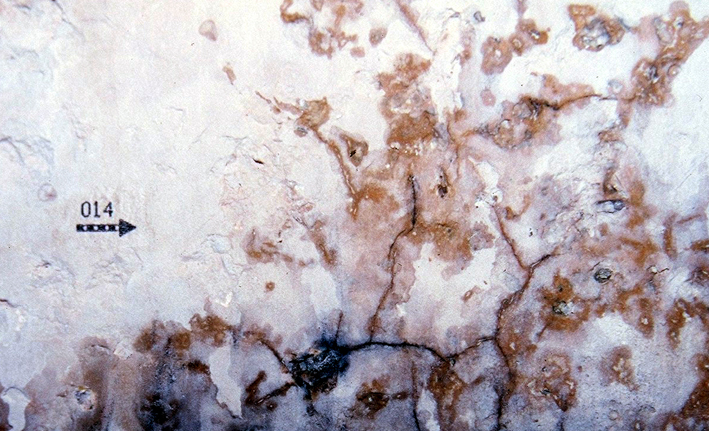
The photograph shows darkened areas within the layers of crust deposits along fissures in the paint layer and topcoat of the plaster. The reason for this is the presence of hygroscopic salts that tend to bind moisture originating from the plaster or from the ambient air. The moisture film will reflect light more giving the surface its darker appearance. | |||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
Revision as of 19:58, 6 January 2013
Author: Nicole Riedl
English Translation by Hans-Jürgen Schwarz andSandra Leithäuser
back to Decay Pattern
Examples of damage by salt progression[edit]
Calcareous concretions (sinter crusts)[edit]
Precipitation of calcium carbonate on the surface of wall paintings begins by a fine white veil and may continue to form a white, dense calcareous concretion. It is characterized by a high stability and strong bond with the painting. The vapor permeability of the wall painting is reduced and the layered crust deposits affects the aesthetic appearance considerably.
Framboidal efflorescence (cauliflower crust)[edit]
The formation of firmly adhering framboidal efflorescence is characteristic for some conditions. The composition may consist of calcium carbonate or gypsum,calcium sulfate dihydrate. Depending on the contaminants present, the efflorescence nay appear whitish, yellowish, reddish or brownish. Biogenic precipitate can be stored within the crust deposits.
Hygroscopic salts[edit]
The photograph shows darkened areas within the layers of crust deposits along fissures in the paint layer and topcoat of the plaster. The reason for this is the presence of hygroscopic salts that tend to bind moisture originating from the plaster or from the ambient air. The moisture film will reflect light more giving the surface its darker appearance.
Powdery salt deposits[edit]
White, loosely adhering salt efflorescence on the plaster and the paint surface. A characteristic of this efflorescence is the formation of small crystalline, soft, powdery salts, which can differ considerably in their chemical composition. The example shows sodium sulfate deposits on a repair plaster made of trass cement.
Scaling due to salt activity[edit]
The crystallizing salts burst the plaster structure. During the phase transition from liquid salt solution to the formation of salt crystals, an expansion takes place and pressure is applied to the adjacent plaster matrix. Hence, entire layers of plaster are lifted from the substructure and become crumbly and fragile.