Calicum nitrate: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
==Solubility== | ==Solubility== | ||
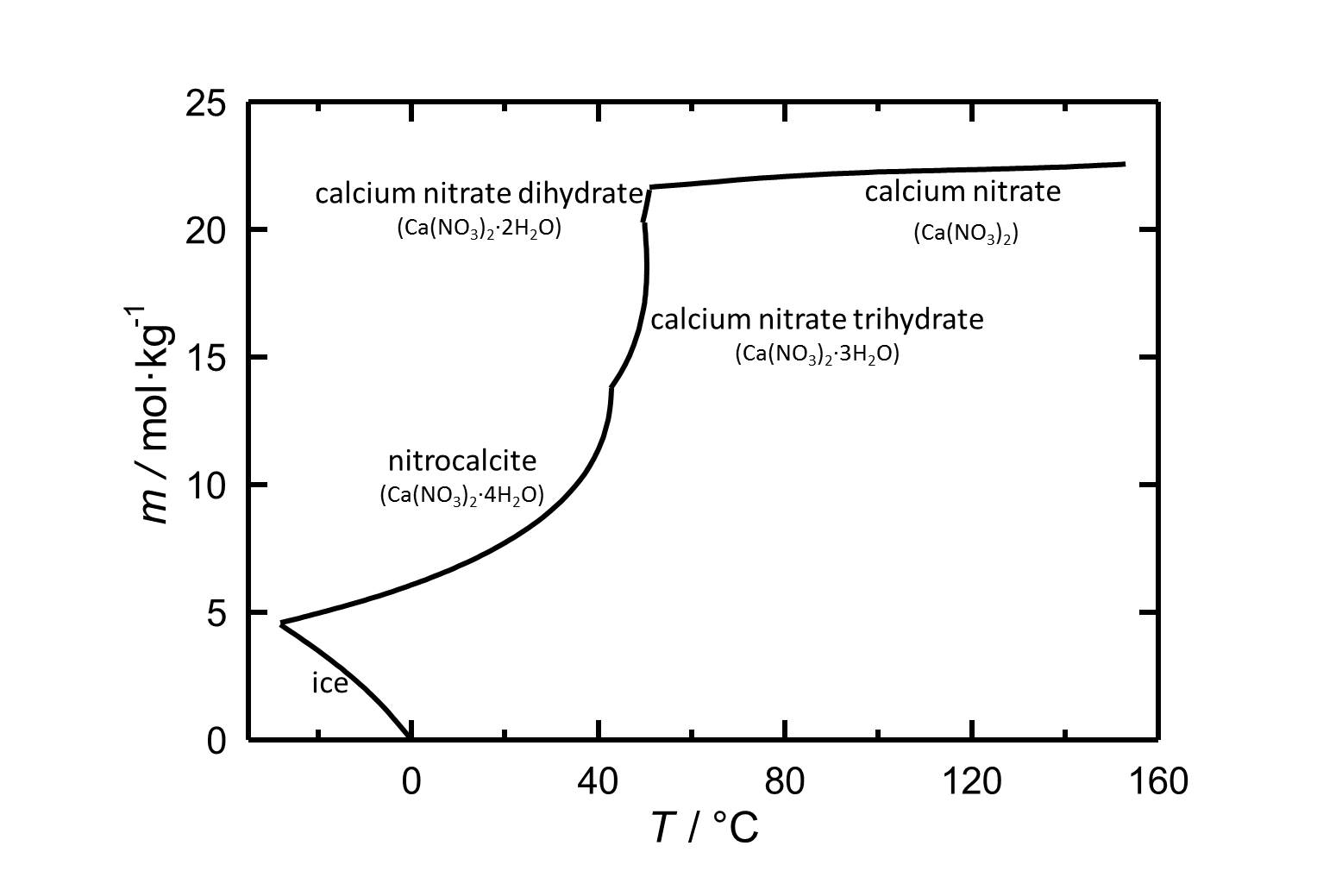
[[Image: | [[Image:Solubility of calcium nitrate in water.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Figure 1: Solubility of calcium nitrate in water. The molality n(Ca(NO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>•xH<sub>2</sub>)•kg(H<sub>2</sub>O)<sup>-1</sup> is plotted against the temperature.]] | ||
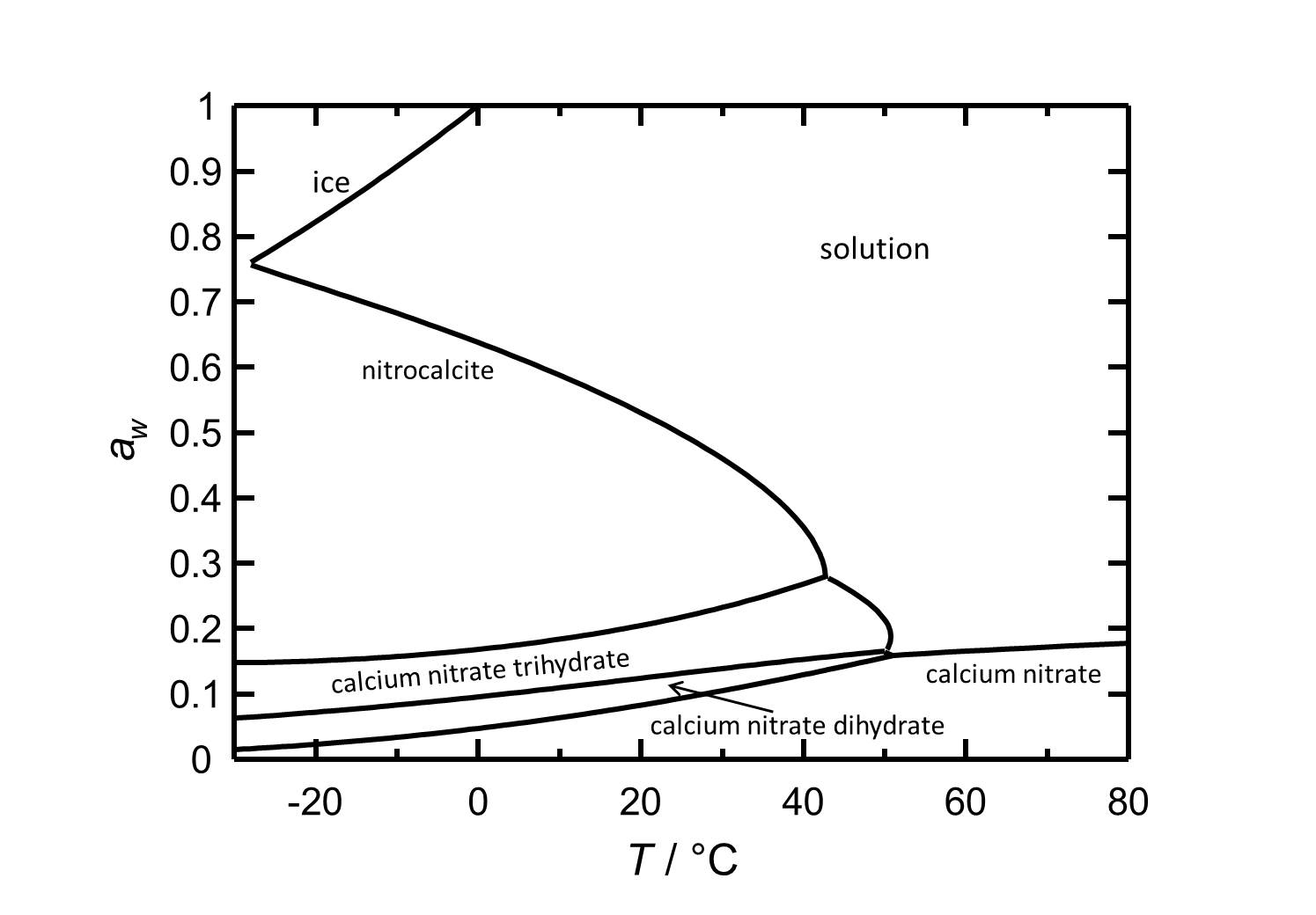
==Hygroscopcity== | ==Hygroscopcity== | ||
Revision as of 13:15, 24 February 2015
Author: Amelie Stahlbuhk
back to Nitrate
| This article will be released soon. |
| Calicum nitrate | |
| Mineralogical name | Calcium nitrate |
| Chemical name | Calcium nitrate |
| Trivial name | |
| Chemical formula | Ca(NO3)2 |
| Other forms | Ca(NO3)2•2H2O (Calcium nitrate dihydrate) Ca(NO3)2•3H2O (Calcium nitrate trihydrate) Ca(NO3)2•4H2O (Nitrocalcite) |
| Crystal system | |
| Crystal structure | |
| Deliquescence humidity 20°C | |
| Solubility (g/l) at 20°C | |
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.483 g/cm3 |
| Molar volume | 66.09 cm3/mol |
| Molar weight | 164.09 g/mol |
| Transparency | |
| Cleavage | |
| Crystal habit | |
| Twinning | |
| Phase transition | |
| Chemical behavior | |
| Comments | |
| Crystal Optics | |
| Refractive Indices | |
| Birefringence | |
| Optical Orientation | |
| Pleochroism | |
| Dispersion | |
| Used Literature | |
| [Robie.etal:1978]Title: Thermodynamic properties of minerals and related substances at 298.15 K and 1 bar pressure and higher temperatures Author: Robie R.A., Hemingway B.S.; Fisher J.A. 
| |
Abstract[edit]
In this article the salt calcium nitrate will be presented. The behavior regarding solubility an hygroscopicity will be shown for caclium nitrate and the different hydrate states.
Solubility[edit]
Hygroscopcity[edit]
References[edit]
Literature[edit]
| [Robie.etal:1978] | Robie R.A., Hemingway B.S.; Fisher J.A. (1978): Thermodynamic properties of minerals and related substances at 298.15 K and 1 bar pressure and higher temperatures. In: U.S. Geol. Surv. Bull, 1452 () |  |