Calcium chloride: Difference between revisions
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
[[Category:Stahlbuhk,Amelie]][[Category:Calcium chloride]] [[Category:Chloride]] [[Category:R-MSteiger]] [[Category: | [[Category:Stahlbuhk,Amelie]][[Category:Calcium chloride]] [[Category:Chloride]] [[Category:R-MSteiger]] [[Category:InReview]] [[Category:Salt]] | ||
Revision as of 18:33, 25 July 2015
Author: Amelie Stahlbuhk
back to Chloride
Abstract[edit]
The different hydrate stages of calcium chloride are presented, as well as their behavior regarding solubility and hygroscopicity.
Hydrate stages[edit]
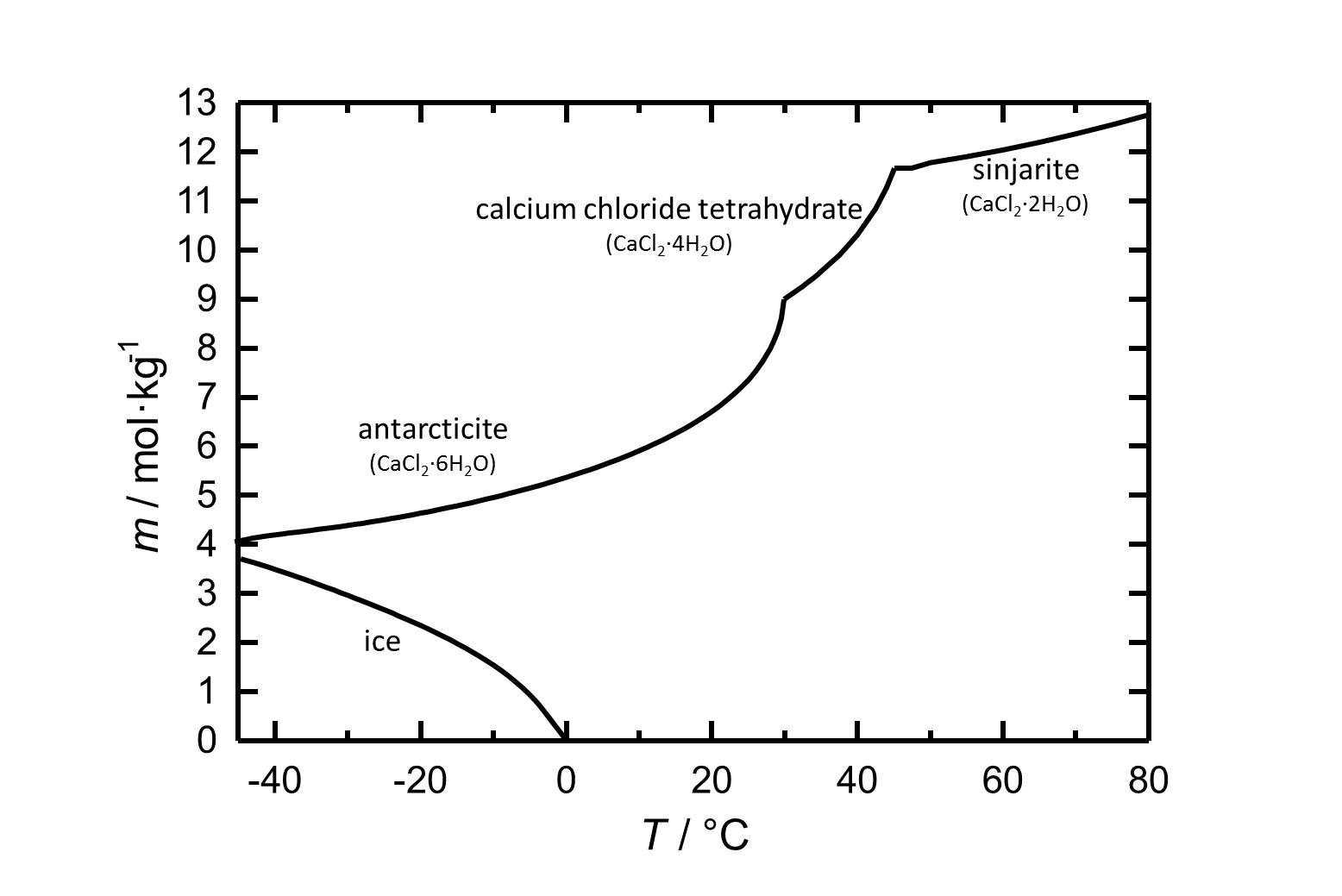
Sinjarite: CaCl2•2H2O
Calcium chloride tetrahydrate: CaCl2•4H2O
Antarcticite: CaCl2•6H2O
Solubility[edit]
Under standard conditions the hexahydrate of calcium chloride Antarcticite is the stable form. The salt has got a high solubility in water which increases with increasing temperatures. The dehydration steps to the calcium chloride tetrahydrate and to sinjarite take place at temperatures of 30 °C and 45 °C, respectively.
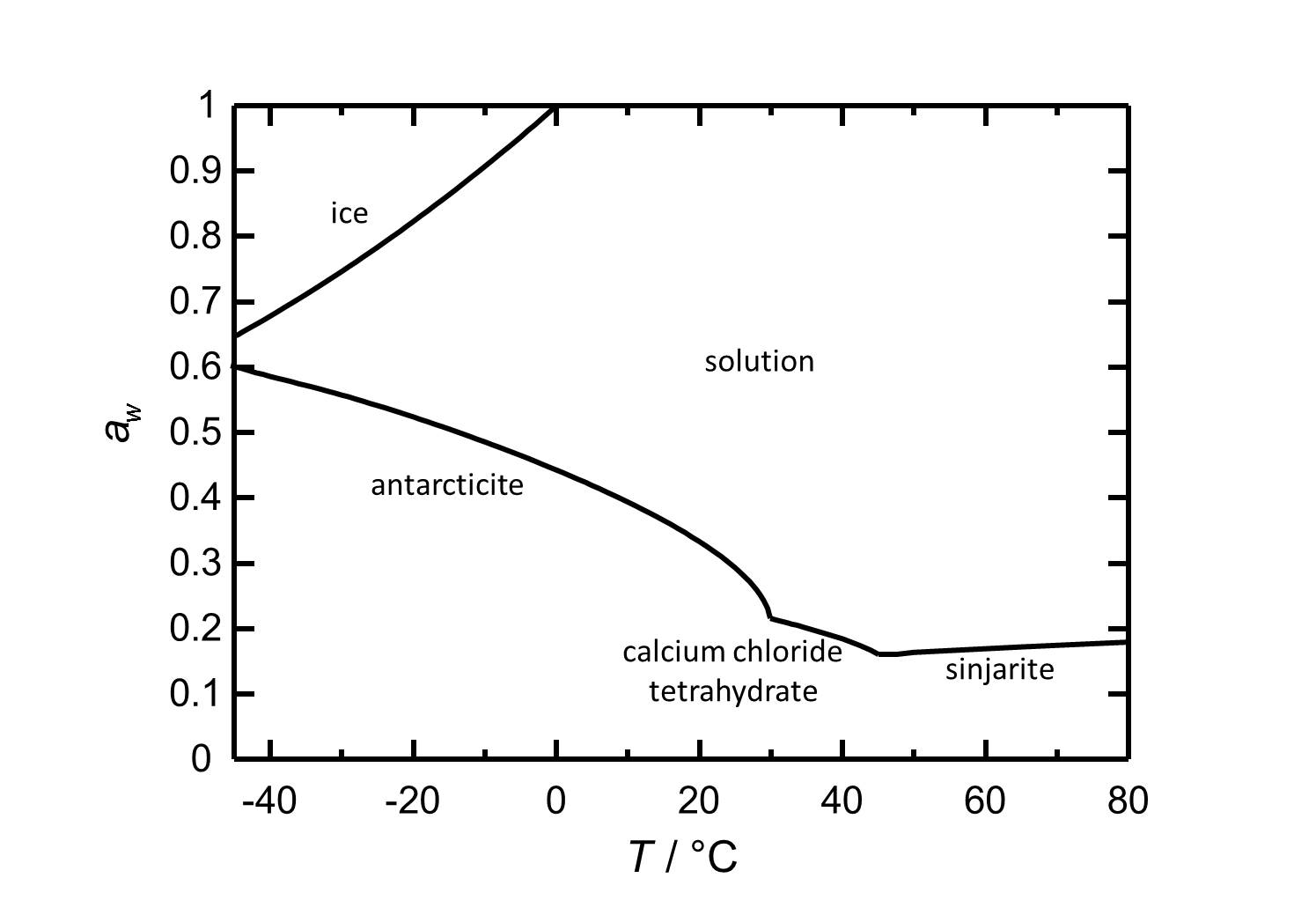
Hygroscopicity[edit]
At room temperature, any Antarcticite present has got a deliquescence humidity of about 30 %. It is also stable up to 30 °C at very low relative humidities, a fact that shows the hygroscopicity of the phase. At room temperature changes in the relative humidity do not provoke phase transitions. Calcium chloride tetrahydrate and Sinjarite have constant deliquescence humidities below 22 % in their temperature ranges.