Deterioration Patterns: Difference between revisions
| (60 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
< | <!--Please check on my translations in the Glossary section- I have researched some terms, but am not entirely sure. --> | ||
Author: [[user:Hschwarz|Hans-Jürgen Schwarz]] | <!-- The English version of this text was edited by Sandra Leithäuser--> | ||
Author: [[user:Hschwarz|Hans-Jürgen Schwarz]]<br> | |||
English version by Sandra Leithäuser | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
back to [[SaltWiki:Community_portal|SaltWiki:Portal]] | back to [[SaltWiki:Community_portal|SaltWiki:Portal]] | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Well documented and well analyzed deterioration patterns are of great importance for the assessment of new damage. This article provides an overview of deterioration patterns, that have been observed in the different material groups. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Material based collections of decay | Material based collections of decay patterns are available for: | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
* [[Stone]] | * [[Stone]] | ||
* [[Architectural Ceramics]], [[Plaster]], [[Rendering]] | * [[Architectural Ceramics]], [[Plaster]], [[Rendering]] | ||
* [[Metal]] | * [[Metal]] | ||
* [[Ceramic Materials]], [[ | * [[Ceramic Materials]], [[Glass]] | ||
* [[Organic Materials]] | * [[Organic Materials]] | ||
--> | --> | ||
* [[Wall | * [[Building Materials]] | ||
* [[Deterioration Patterns Wallpaintings|Wall Paintings]] | |||
== Glossary of | == Glossary of Salt Efflorescences == | ||
Efflorescences are whitish, powdery or whisker-like crystals on the surface of porous materials. In most cases efflorescences are poorly cohesive and in general they are constituted by soluble salt crystals. On wall paintings, mortar, plaster, ceramic and natural stone, efflorescences repeatedly display certain typical forms. These are briefly characterized as follows: | |||
''' | <br clear = all> | ||
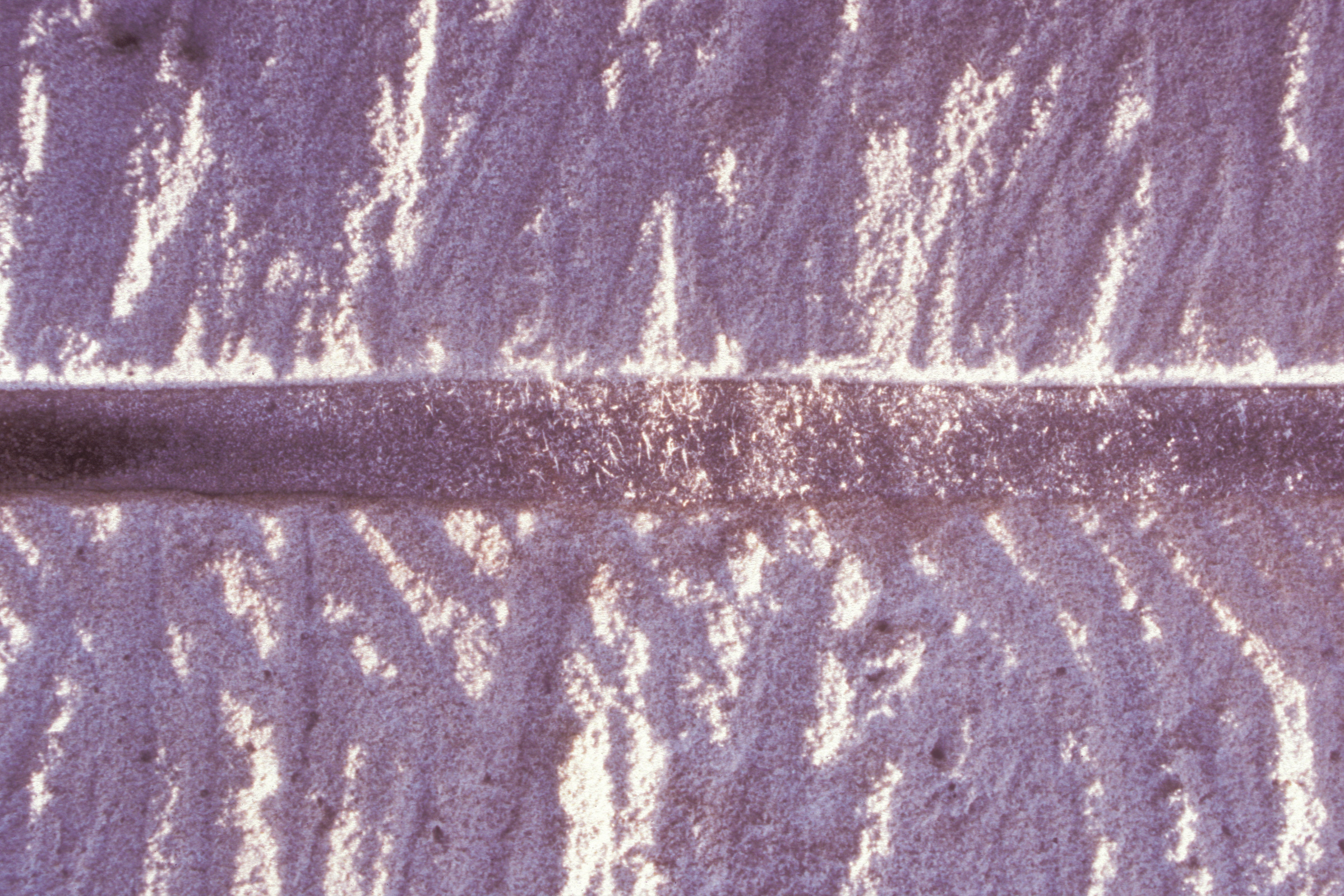
'''Whiskers''': a few microns thick to centimeters long, columnar, often curved crystals. Under specific conditions, crystals, which do not typically exhibit needle-building habits, grow as fine, hair-like shapes, the so-called whiskers. Whiskers have been observed developing from a variety of substances, e.g., metals, salts, etc. Their diameters range between 0.01 and 100 microns, while their length can reach up to a few centimeters. They grow preferentially in the longitudinal direction, while the growth on the lateral crystal plane is either suppressed or, to some extent, still in progress. Some whiskers accommodate a single, or a few, screw dislocations along their axis, causing a spiral growth at the tip, so that material along the lateral plane has to be transported to the tip. Some whiskers do not have screw dislocations, where the preferred growth takes place at the top- caused by a different mechanism. Finally, there are whiskers that do not grow at the top, but at their base, pushing the growing crystal upwards. | |||
<br clear =all> | |||
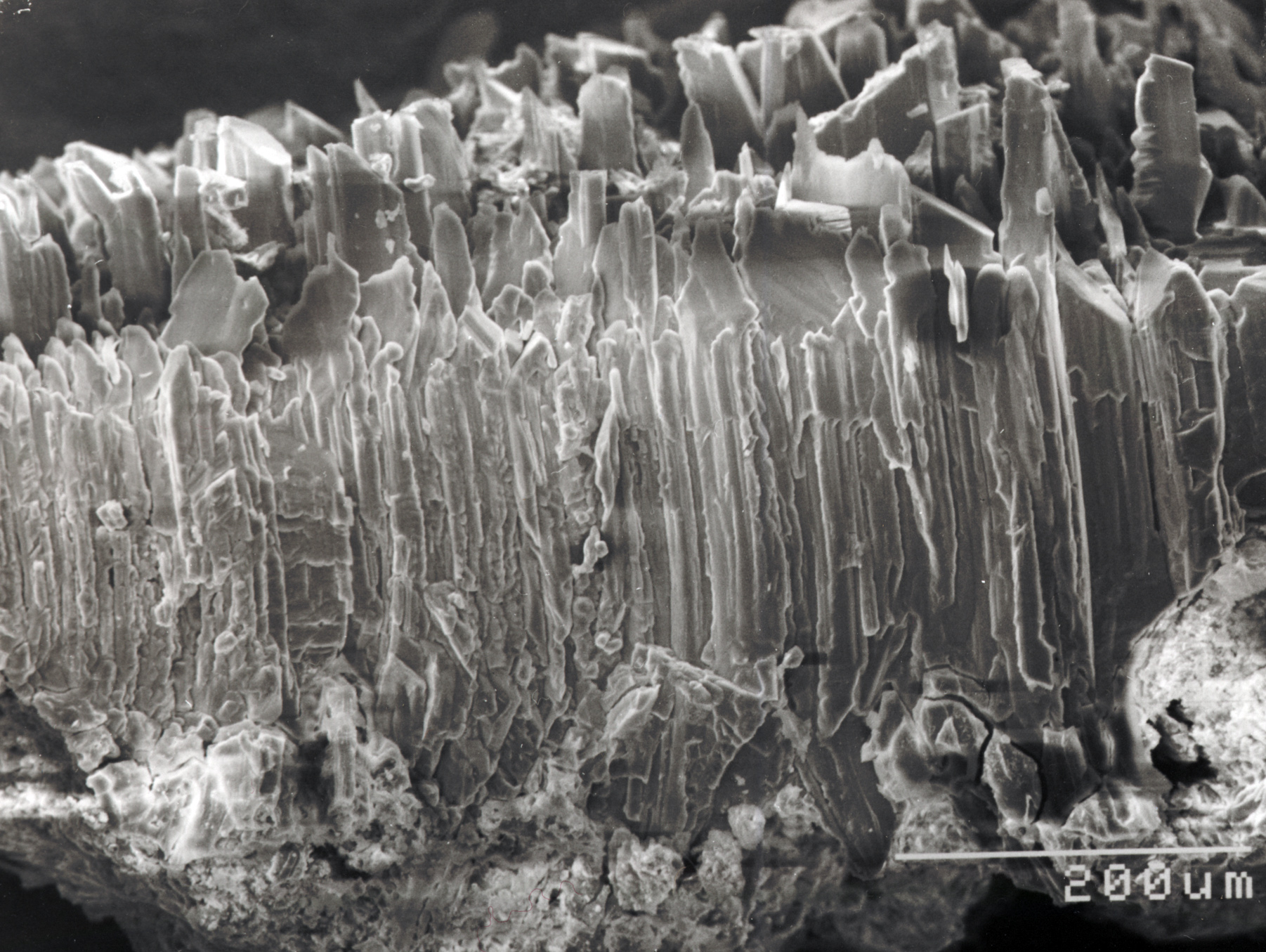
[[file:Arnold-Swi 04.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Whiskers are long, thin, sometimes curved crystals, here NaCl whiskers (from <bib id="Arnold.etal:1991"/>)]] | |||
<br clear = all> | <br clear = all> | ||
<br> '''Feathery - Fluffy efflorescence''': very loose, fluffy or cotton-like efflorescence, usually consisting of bent whiskers. | |||
<br clear = all> | <br clear = all> | ||
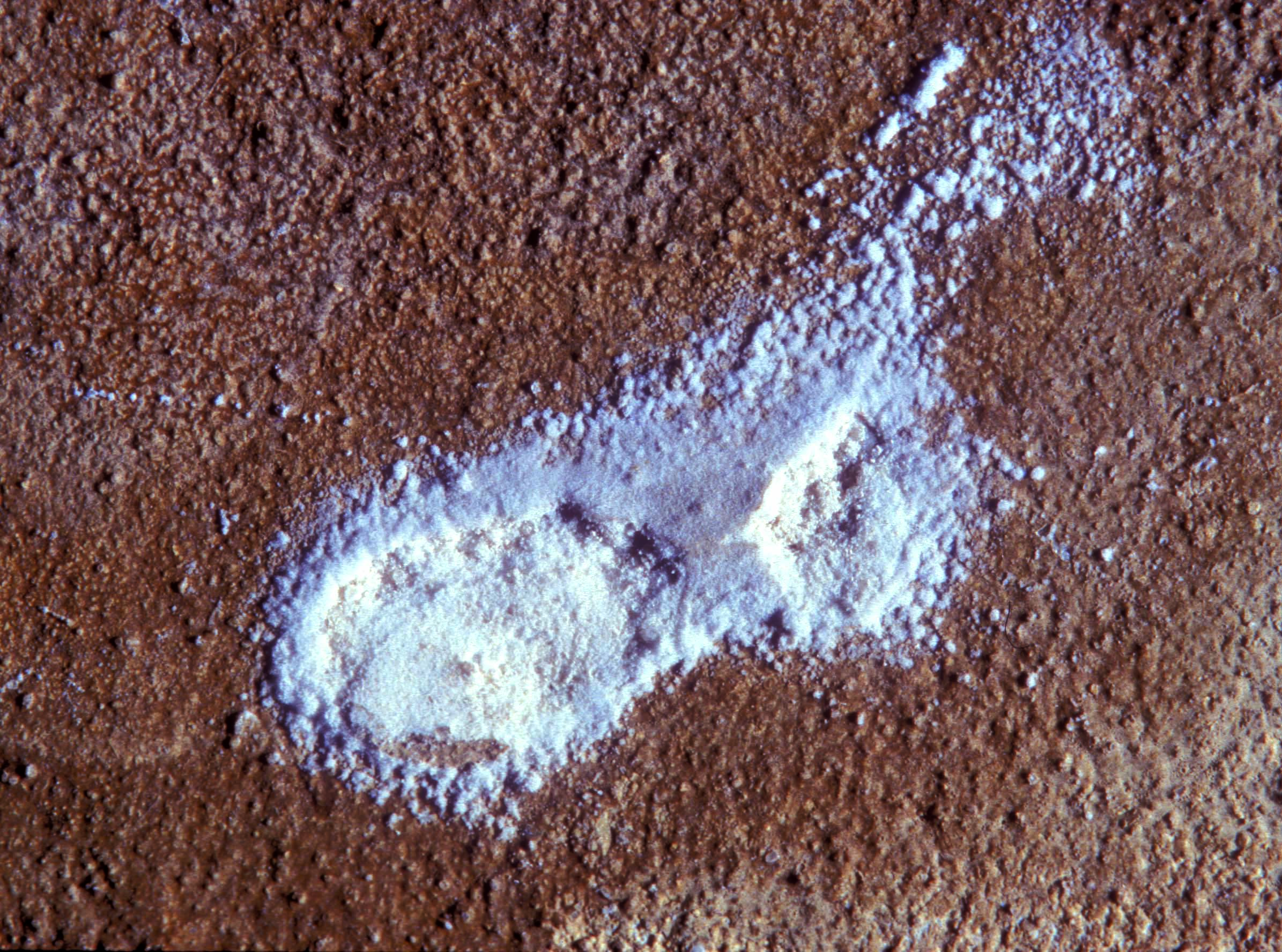
[[file: | [[file:KNO3-SalzflaumKoenigslutter.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Efflorescence made of KNO<sub>3</sub>, the crystals are whiskers]] | ||
<br clear = all> | <br clear = all> | ||
<br clear = all> | |||
''' | '''Acicular crystals-bristly efflorescence''': loose columnar whiskers, more or less perpendicular to the surface, 0.1 to several millimeters long, often only visible in raking light. | ||
<br clear = all> | |||
[[file:IdensenThenardit_ausbluehung_aussen.jpg|thumb|left|right|400px|Salt crystals on a masonry joint; the individual crystals are whiskers]] | |||
<br clear = all> | <br clear = all> | ||
<br clear = all> | |||
''' | '''Powdery efflorescence''': white, mealy, loose to dense or fluffy coating. Powdery efflorescence will develop differently depending on the type of salt crystallizing. Some salts, especially the less soluble ones such as gypsum, can bloom in this very fine form as soon as they crystallize. However, in the case of sodium sulfate this form of efflorescence results from the dehydration of the originally hydrated salt. | ||
<br clear = all> | |||
[[file:Eilsumpudrigeausbluehungen.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Powdery efflorescences of sodium sulfate]] | |||
<br clear = all> | <br clear = all> | ||
[[file: | <br clear = all> | ||
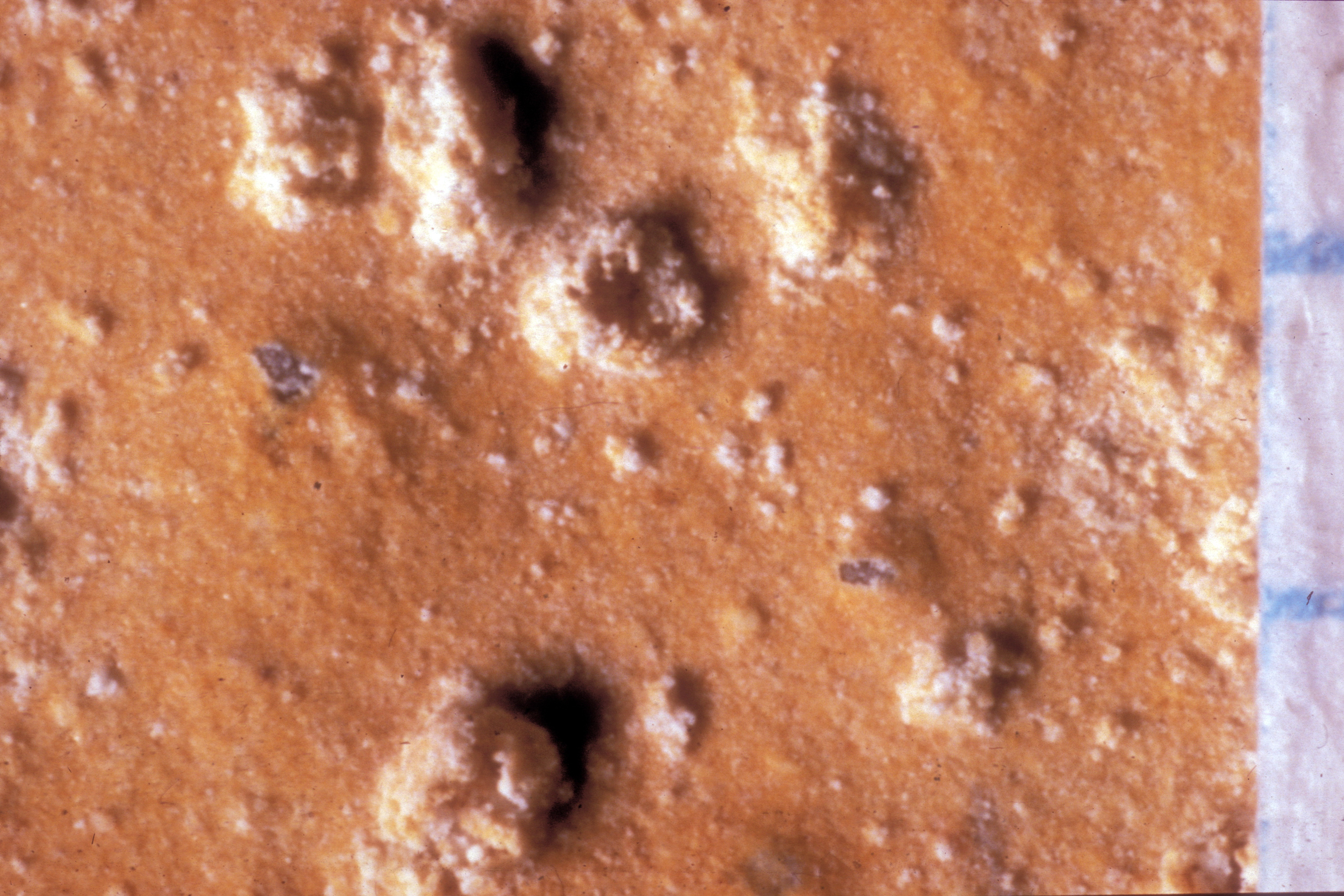
'''Salt pustules''': separate, loose to compact salt crystals, to about 1 mm diameter. | |||
<br clear = all> | |||
[[file:Salzpusteln.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Salt-induced pustules on a wall painting]] | |||
'''Salt crust''' : | <br clear = all> | ||
<br clear = all> | |||
'''Salt crust''' : crusts can be formed by soluble salts when they are highly concentrated developing salt aggregates with planar cohesion and very variable thicknesses (a few microns to mm) | |||
<br clear = all> | |||
[[file:Treppe_bei_St.Andreas_Hildesheim_Salzkruste.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Salt crust caused by de-icing salt]] | |||
<br clear = all> | <br clear = all> | ||
'''White loose crust''' (sugary crust): | <br clear = all> | ||
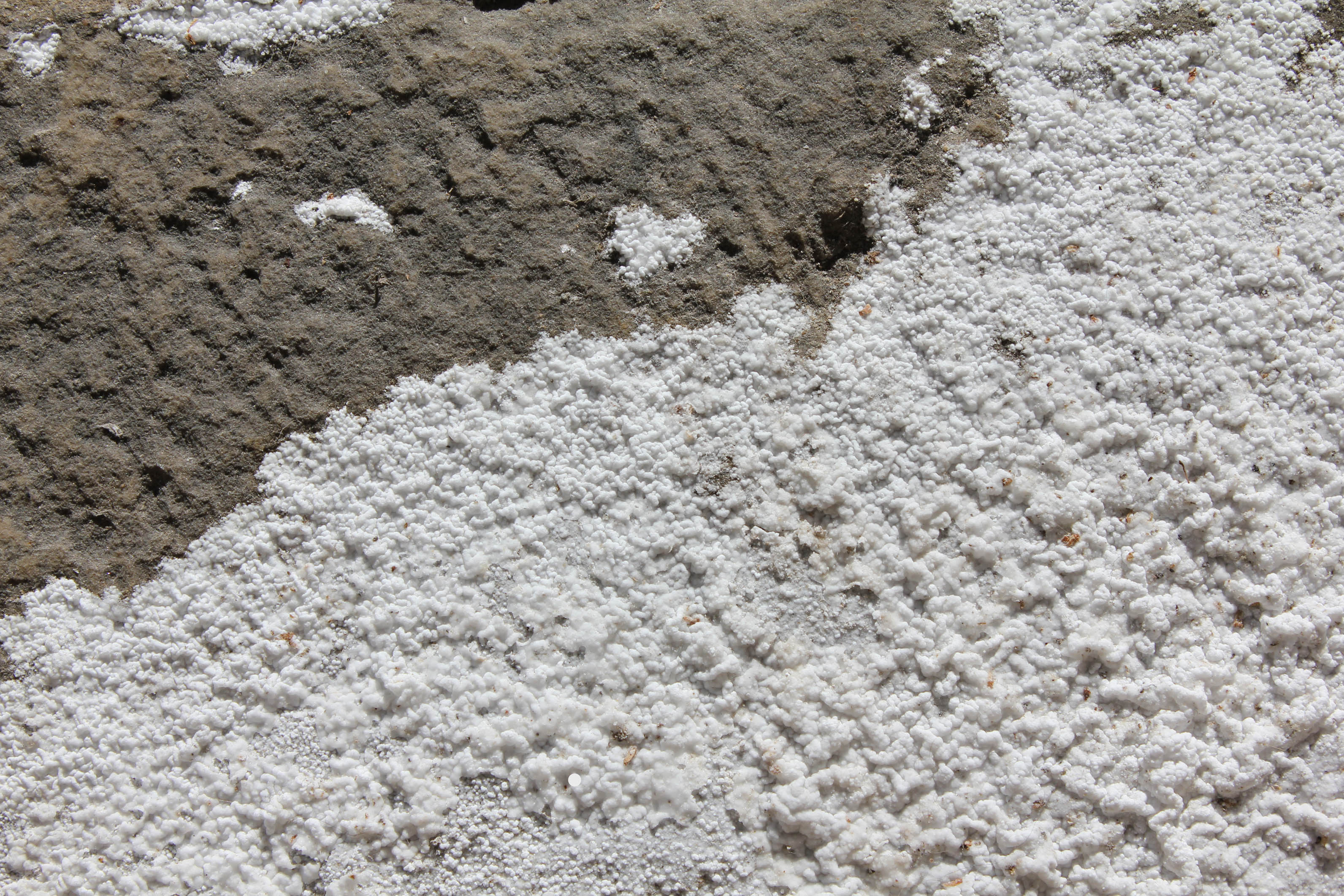
'''White loose crust''' (sugary crust): consists of individuals that are visible to the naked eye or low magnification as glass-clear crystals. Sugary crusts usually form in a moisture film. However, they can crystallize from a salt efflorescence that takes up water from the surrounding air, undergoing dissolution and followed by recrystallizing as the environment dries. | |||
<br clear = all> | |||
[[file:Strahlsund Kochsalz-Kruste.jpg|thumb|left|400px| Halite crust on an exterior wall in Strahlsund]] | |||
<br clear = all> | <br clear = all> | ||
<br clear = all> | |||
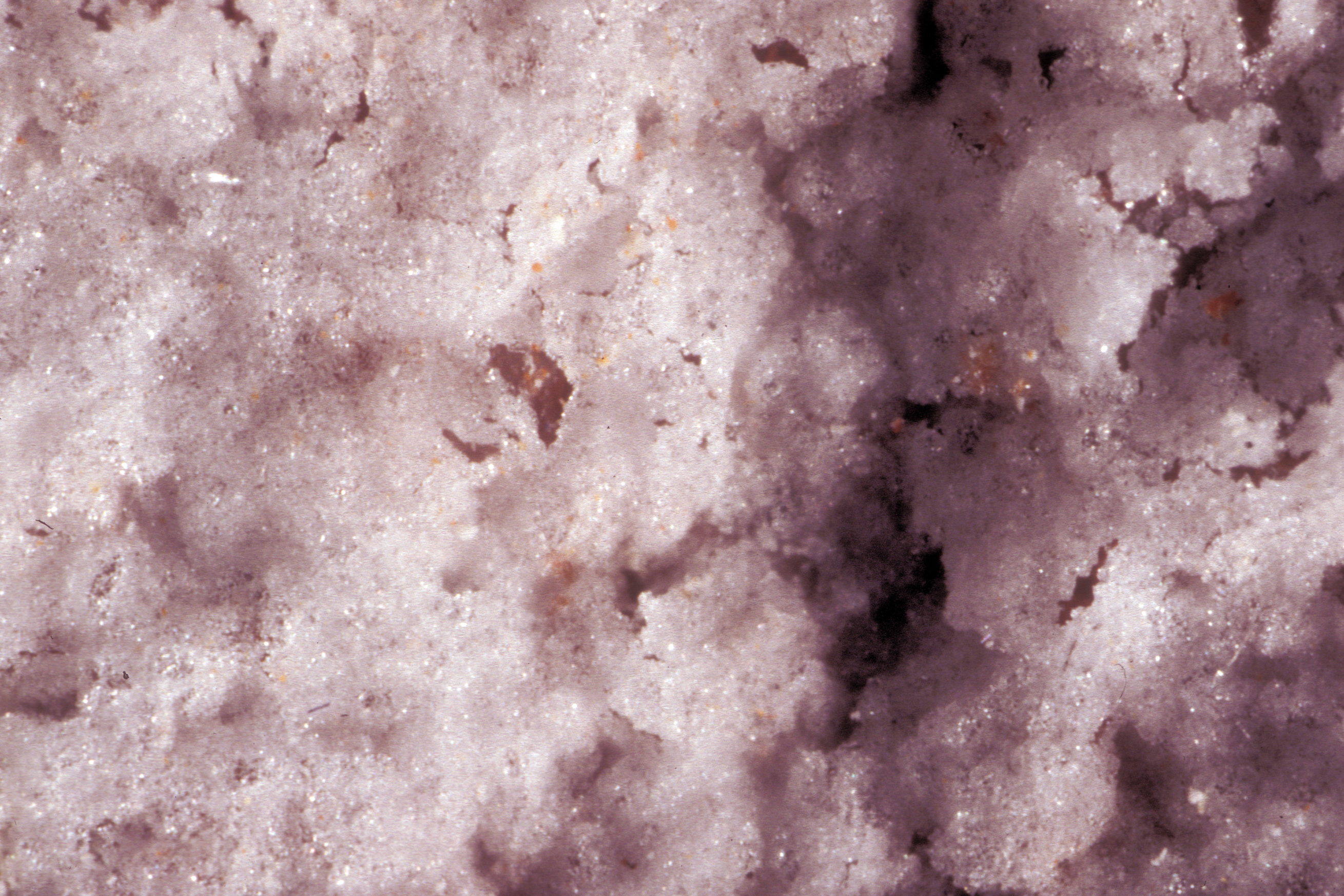
'''Satin | '''Satin crust''': flat, shiny crust of salt. Thick, shiny crusts of gypsum are formed only by repeated recrystallization cycles over longer periods of time. | ||
<br clear = all> | |||
[[file:REM Seidenglanzkruste-mittel.jpg|thumb|left|400px|SEM photo of a satin like crust]] | |||
<br clear = all> | |||
<br clear = all> | |||
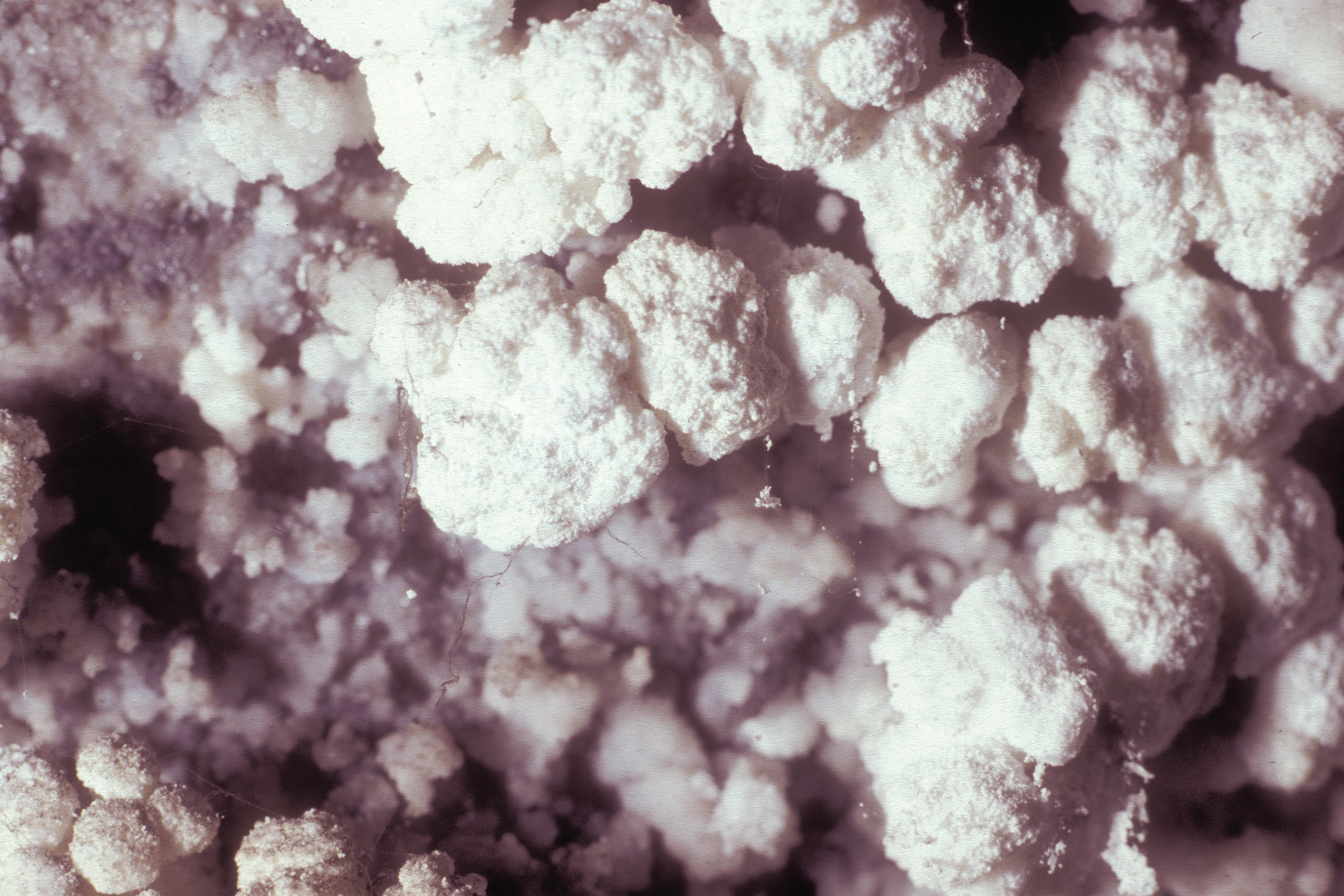
'''Framboidal or botroidal crusts''': crust of white, spherical aggregates- its surface resembles that of a raspberry or blackberry or even a cauliflower. Botroidal crusts occur preferentially along small defects (e.g., cracks) on an otherwise relatively dense plaster surface. They also can form as separate units on dense stones. | |||
<br clear = all> | |||
[[file:Gips Blumenkohlkruste 2.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Framboidal efflorescences]] | |||
<br clear = all> | <br clear = all> | ||
<br clear = all> | <br clear = all> | ||
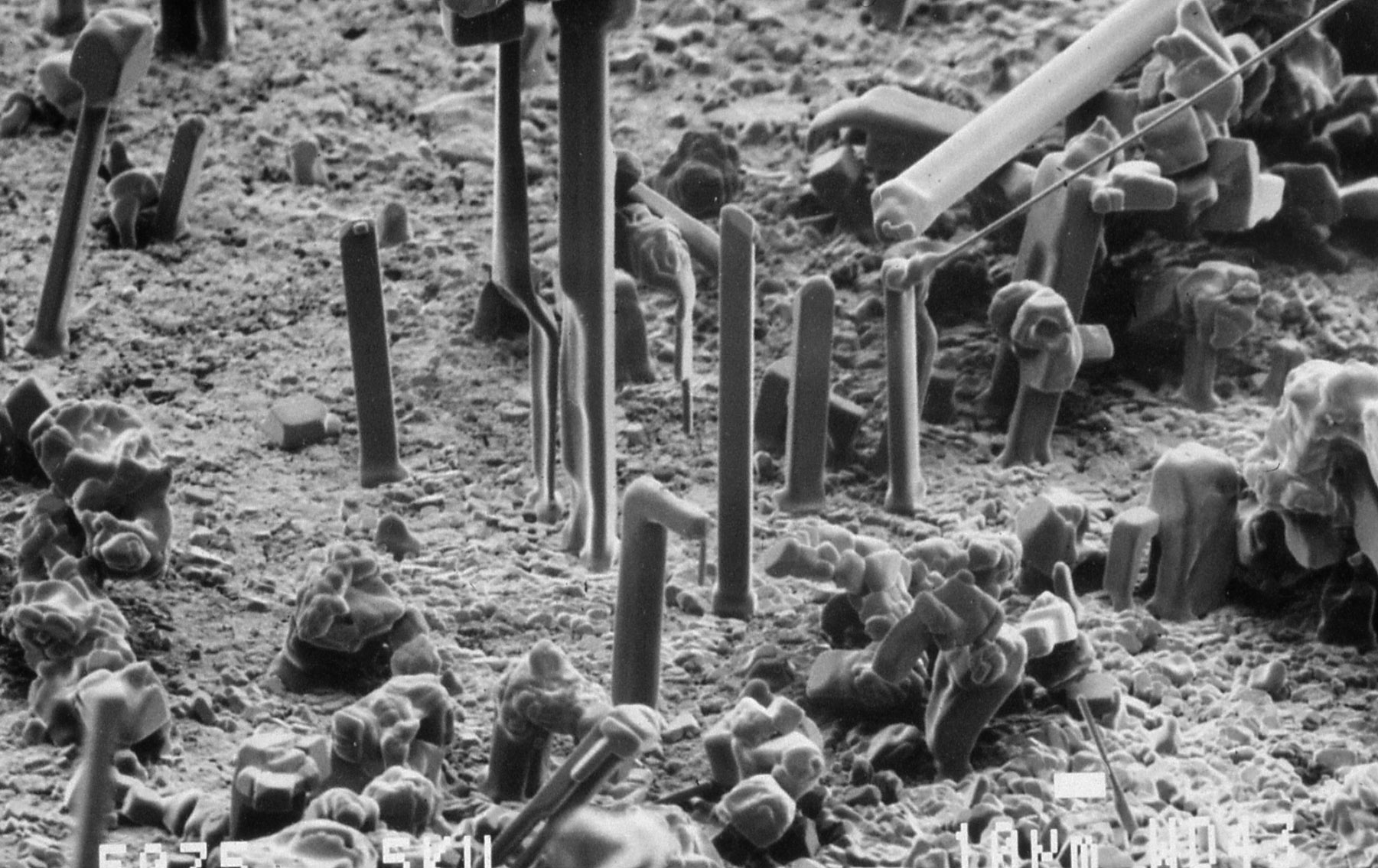
''' | '''Fibrous crust:''' crust composed of densely packed whiskers, perpendicular to the substrate. They usually develop on moist substrates. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== | == Habit == | ||
* | *The crystal habit describes the proportions and shape of crystals. | ||
<br> | <br> The habit of salts will change depending on the conditions during their formation. | ||
Due to the crystal structure and the typical mineral and surface combinations, salts change in their physical appearance. On occasions, changes can also be caused by unilateral growth. We describe these mineral forms as follows: | |||
*''' | *'''isometric''' forms, if the development into all three spatial directions is approximately of the same size e.g.. all cubic crystals. | ||
*''' | *'''one-dimensional elongated''' forms: columnar, acicular, hair-like (whisker), fibrous, such as tourmaline, rutile, asbestos. | ||
*''' | *'''two-dimensional elongated''' forms: tabular, lamellar, foliated, scaly, micaceous, e.g.. barite and mica. | ||
*''' | *'''dendritic''' forms occur in the case of an incomplete crystal growth, developing plant-like shapes. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== | == Formation of salt crystals, according to Arnold == | ||
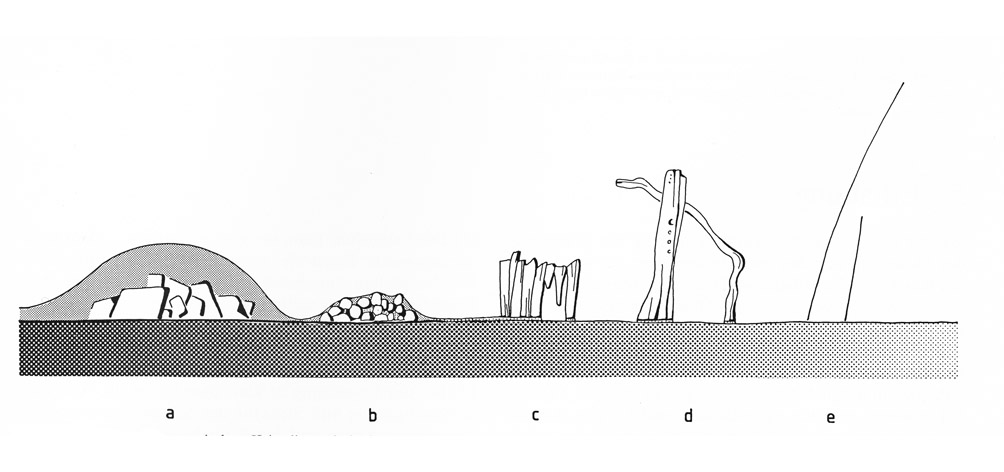
According to <bib id="Arnold:1992" /> the crystal morphology (habit) can be subdivided into five groups depending on the moisture condition present (see figure): | |||
a) | a) Multidirectional growth, large crystals with equilibrium shapes are formed on a wet surface as long as the growing crystals are immersed in the solution. The solution covers the whole surface or parts of it as a dense film. | ||
b) | b) A granular crust of isometric crystals forms on a wet substrate, while the crystals are immersed in the solution film and are growing into multiple directions. | ||
c) | c) A fibrous crust forms on a medium moist substrate that is completely covered by the solution film. The columnar crystals grow from their base that is still in contact with the nutrient solution so that the dry crystals are moved upward. | ||
d) | d) Columnar, thick whisker-like crystals grow on the humid surface and out of small pools of the solution. | ||
e) | e) Very thin whiskers grow out of "solution drops" on the now nearly dry surface. The result is a fluffy salt efflorescence. | ||
Salts can form their characteristic crystals under undisturbed crystallization conditions and when a sufficient supply of the salt solution is available. These crystals are called idiomorphic. Hypidiomorphic crystals are those that are only partially idiomorphic, while xenomorphic crystals refers to those whose shape does not resemble the intriinsic one. | |||
[[Image:Salzkristallisation Feuchteregime.jpg|thumb|center|600px|Relationship between crystal morphology and moisture regime (after <bib id="Arnold:1992"/>) ]] | |||
== Literature == | == Literature == | ||
< | <biblist/> | ||
[[Category:Schwarz,Hans-Jürgen]][[Category:R-CBlaeuer]] [[Category:saltdamage]][[Category:approved]][[Category:Decay_Pattern:Others]][[Category:Decay_Pattern:Ceramics]][[Category:Decay_Pattern:Glas]][[Category:Decay_Pattern:Pottery]][[Category:Decay_Pattern:Metal]][[Category:Decay_Pattern:Plaster]][[Category:Decay_Pattern:Natural_Stone]][[Category:Alveolarweathering]][[Category:Decay_Pattern:Organic_Materials]][[Category:Decay_Pattern:Wall_Paintings]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:15, 19 March 2023
Author: Hans-Jürgen Schwarz
English version by Sandra Leithäuser
back to SaltWiki:Portal
Introduction[edit]
Well documented and well analyzed deterioration patterns are of great importance for the assessment of new damage. This article provides an overview of deterioration patterns, that have been observed in the different material groups.
Material based collections of decay patterns are available for:
Glossary of Salt Efflorescences[edit]
Efflorescences are whitish, powdery or whisker-like crystals on the surface of porous materials. In most cases efflorescences are poorly cohesive and in general they are constituted by soluble salt crystals. On wall paintings, mortar, plaster, ceramic and natural stone, efflorescences repeatedly display certain typical forms. These are briefly characterized as follows:
Whiskers: a few microns thick to centimeters long, columnar, often curved crystals. Under specific conditions, crystals, which do not typically exhibit needle-building habits, grow as fine, hair-like shapes, the so-called whiskers. Whiskers have been observed developing from a variety of substances, e.g., metals, salts, etc. Their diameters range between 0.01 and 100 microns, while their length can reach up to a few centimeters. They grow preferentially in the longitudinal direction, while the growth on the lateral crystal plane is either suppressed or, to some extent, still in progress. Some whiskers accommodate a single, or a few, screw dislocations along their axis, causing a spiral growth at the tip, so that material along the lateral plane has to be transported to the tip. Some whiskers do not have screw dislocations, where the preferred growth takes place at the top- caused by a different mechanism. Finally, there are whiskers that do not grow at the top, but at their base, pushing the growing crystal upwards.

Author: Arnold, Andreas; Zehnder, Konrad
 )
)
Feathery - Fluffy efflorescence: very loose, fluffy or cotton-like efflorescence, usually consisting of bent whiskers.
Acicular crystals-bristly efflorescence: loose columnar whiskers, more or less perpendicular to the surface, 0.1 to several millimeters long, often only visible in raking light.
Powdery efflorescence: white, mealy, loose to dense or fluffy coating. Powdery efflorescence will develop differently depending on the type of salt crystallizing. Some salts, especially the less soluble ones such as gypsum, can bloom in this very fine form as soon as they crystallize. However, in the case of sodium sulfate this form of efflorescence results from the dehydration of the originally hydrated salt.
Salt pustules: separate, loose to compact salt crystals, to about 1 mm diameter.
Salt crust : crusts can be formed by soluble salts when they are highly concentrated developing salt aggregates with planar cohesion and very variable thicknesses (a few microns to mm)
White loose crust (sugary crust): consists of individuals that are visible to the naked eye or low magnification as glass-clear crystals. Sugary crusts usually form in a moisture film. However, they can crystallize from a salt efflorescence that takes up water from the surrounding air, undergoing dissolution and followed by recrystallizing as the environment dries.
Satin crust: flat, shiny crust of salt. Thick, shiny crusts of gypsum are formed only by repeated recrystallization cycles over longer periods of time.
Framboidal or botroidal crusts: crust of white, spherical aggregates- its surface resembles that of a raspberry or blackberry or even a cauliflower. Botroidal crusts occur preferentially along small defects (e.g., cracks) on an otherwise relatively dense plaster surface. They also can form as separate units on dense stones.
Fibrous crust: crust composed of densely packed whiskers, perpendicular to the substrate. They usually develop on moist substrates.
Habit[edit]
- The crystal habit describes the proportions and shape of crystals.
The habit of salts will change depending on the conditions during their formation.
Due to the crystal structure and the typical mineral and surface combinations, salts change in their physical appearance. On occasions, changes can also be caused by unilateral growth. We describe these mineral forms as follows:
- isometric forms, if the development into all three spatial directions is approximately of the same size e.g.. all cubic crystals.
- one-dimensional elongated forms: columnar, acicular, hair-like (whisker), fibrous, such as tourmaline, rutile, asbestos.
- two-dimensional elongated forms: tabular, lamellar, foliated, scaly, micaceous, e.g.. barite and mica.
- dendritic forms occur in the case of an incomplete crystal growth, developing plant-like shapes.
Formation of salt crystals, according to Arnold[edit]
According to [Arnold:1992]Title: Salze: Lästige weiße Ausblühungen oder Hauptschadensursache?
Author: Arnold, Andreas the crystal morphology (habit) can be subdivided into five groups depending on the moisture condition present (see figure):
the crystal morphology (habit) can be subdivided into five groups depending on the moisture condition present (see figure):
a) Multidirectional growth, large crystals with equilibrium shapes are formed on a wet surface as long as the growing crystals are immersed in the solution. The solution covers the whole surface or parts of it as a dense film.
b) A granular crust of isometric crystals forms on a wet substrate, while the crystals are immersed in the solution film and are growing into multiple directions.
c) A fibrous crust forms on a medium moist substrate that is completely covered by the solution film. The columnar crystals grow from their base that is still in contact with the nutrient solution so that the dry crystals are moved upward.
d) Columnar, thick whisker-like crystals grow on the humid surface and out of small pools of the solution.
e) Very thin whiskers grow out of "solution drops" on the now nearly dry surface. The result is a fluffy salt efflorescence.
Salts can form their characteristic crystals under undisturbed crystallization conditions and when a sufficient supply of the salt solution is available. These crystals are called idiomorphic. Hypidiomorphic crystals are those that are only partially idiomorphic, while xenomorphic crystals refers to those whose shape does not resemble the intriinsic one.
Author: Arnold, Andreas
 )
)Literature[edit]
| [Arnold.etal:1991] | Arnold, Andreas; Zehnder, Konrad (1991): Monitoring Wall Paintings Affected by soluble Salts. In: Cather, Sharon (eds.): The Conservation of Wall Paintings: Proceedings of a symposium organized by the Coutrauld Institut of Art and the Getty Conservation Institute, London, July 13-16, The Getty Conservation Institute, 103-136. |  |
| [Arnold:1992] | Arnold, Andreas (1992): Salze: Lästige weiße Ausblühungen oder Hauptschadensursache?. In: Jahresberichte Steinzerfall - Steinkonservierung, 2 (), 1-9 |  |