Calcium chloride: Difference between revisions
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
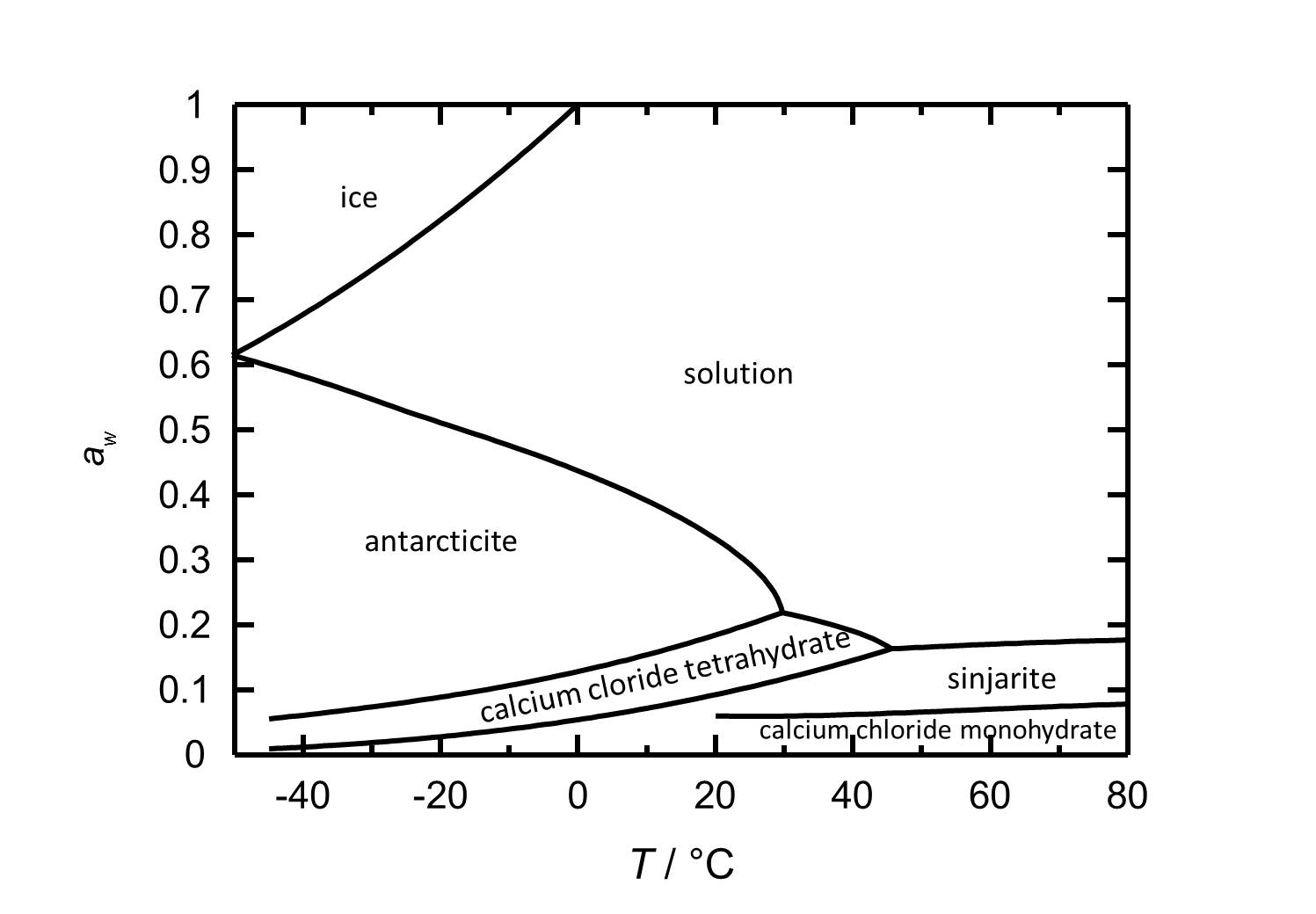
[[file:D | [[file:D CaCl2 e.jpg|thumb|left|800px|Figure 2: Deliquescence behaviour of calcium chloride in the temperature range from -45 to 80 °C. The water activity ''a<sub>w</sub>'' is plotted against the temperature.]] | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
At room temperature | At room temperature the present phase [[Antarcticite]] has got a deliquescence humidity of about 30 %. The deliquescence behavior depends on the temperature as the deliquescence humidity decreases with increasing temperature. Changing the relative humidity at 20 °C, calcium chloride tetrahydrate forms at values below 18 % RH. The dehydration to the Dihydrate ([[sinjarite]]) and the monohydrate occurs at 9 % RH and 6 % RH, respectively. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 11:56, 2 November 2015
Author: Amelie Stahlbuhk
back to Chloride
Abstract[edit]
The different hydrate stages of calcium chloride are presented, as well as their behavior regarding solubility and hygroscopicity.
Hydrate stages[edit]
Sinjarite: CaCl2•2H2O
Calcium chloride tetrahydrate: CaCl2•4H2O
Antarcticite: CaCl2•6H2O
Solubility[edit]
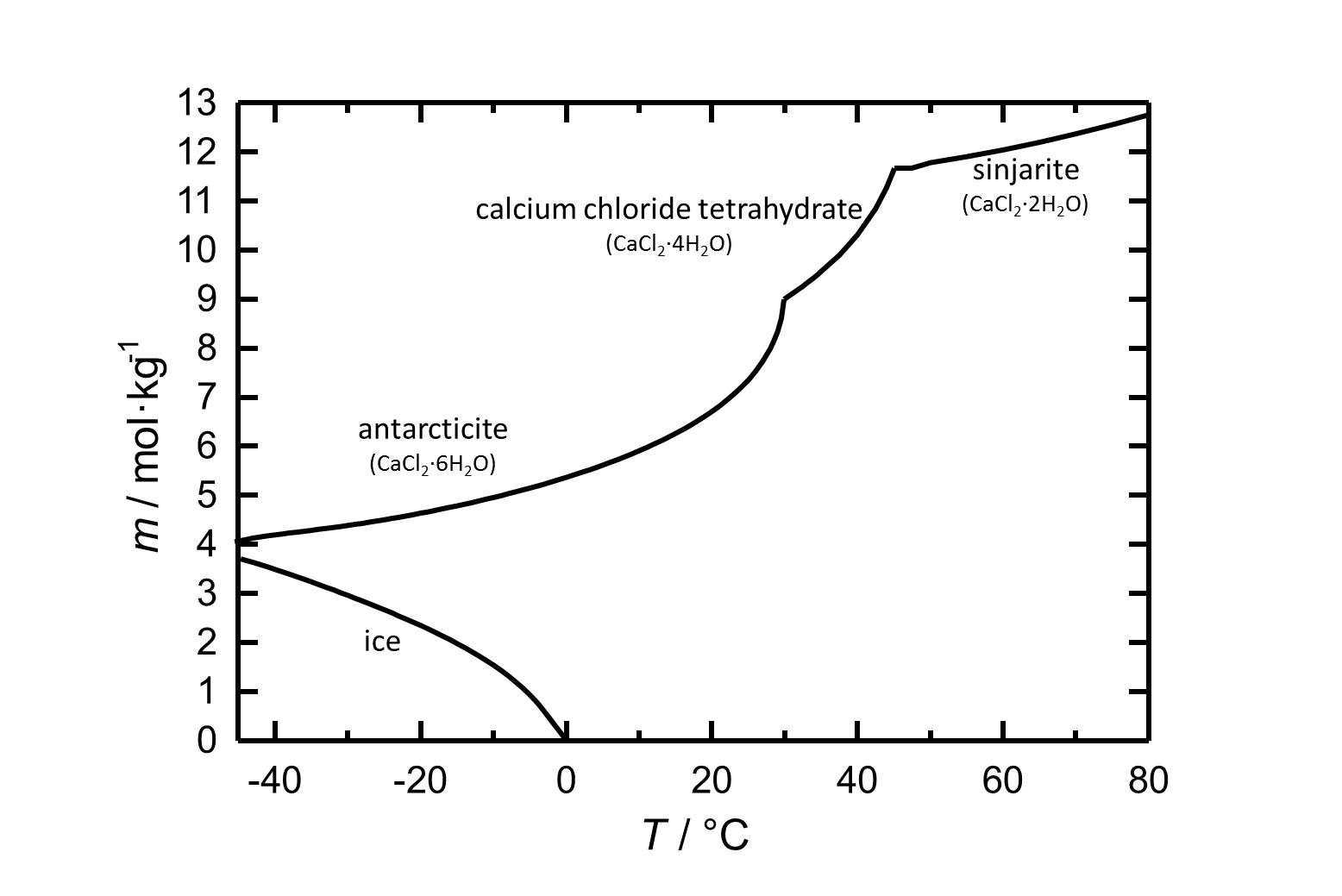
Under standard conditions the hexahydrate of calcium chloride Antarcticite is the stable form. The salt has got a high solubility in water which increases with increasing temperatures. The dehydration steps to the calcium chloride tetrahydrate and to sinjarite take place at temperatures of 30 °C and 45 °C, respectively.
Hygroscopicity[edit]
At room temperature the present phase Antarcticite has got a deliquescence humidity of about 30 %. The deliquescence behavior depends on the temperature as the deliquescence humidity decreases with increasing temperature. Changing the relative humidity at 20 °C, calcium chloride tetrahydrate forms at values below 18 % RH. The dehydration to the Dihydrate (sinjarite) and the monohydrate occurs at 9 % RH and 6 % RH, respectively.